
The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by METANET, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]metanet.ch.

https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.Patterns
It is designed to work with patterned data. Famous examples of problems related to patterned data are:
It allows for single or joint modeling of, for instance, genes and proteins.
Patterns package and dedicated to get specific
features for the inferred network such as
sparsity, robust links, high
confidence links or stable through resampling
links.
lars packageglmnet package. An
unweighted and a weighted version of the algorithm are availablespls packageelasticnet
packagec060
package implementation of stability selectionc060 package implementation of stability
selection that I created for the packagelars package
with light random Gaussian noise added to the explanatory variablesselectboost
package. The selectboost algorithm looks for the more stable links
against resampling that takes into account the correlated structure of
the predictorsselectboost.The weights are viewed as a penalty factors in the penalized regression model: it is a number that multiplies the lambda value in the minimization problem to allow differential shrinkage, Friedman et al. 2010, equation 1 page 3. If equal to 0, it implies no shrinkage, and that variable is always included in the model. Default is 1 for all variables. Infinity means that the variable is excluded from the model. Note that the weights are rescaled to sum to the number of variables.
A word for those that have been using our seminal work, the
Cascade package that we created several years ago and that
was a very efficient network reverse engineering tool for cascade
networks (Jung, N., Bertrand, F., Bahram, S., Vallat, L., and
Maumy-Bertrand, M. (2014), https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt705, https://cran.r-project.org/package=Cascade, https://github.com/fbertran/Cascade and https://fbertran.github.io/Cascade/).
The Patterns package is more than (at least) a threeway
major extension of the Cascade package :
Cascade package only 1 group for each timepoint could be
created, which prevented the users to create homogeneous clusters of
genes in datasets that featured more than a few dozens of genes.Cascade package only 1 shape
was provided:
Cascade.Hence the Patterns package should be viewed more as a
completely new modelling tools than as an extension of the
Cascade package.
This website and these examples were created by F. Bertrand and M. Maumy-Bertrand.
You can install the released version of Patterns from CRAN with:
install.packages("Patterns")You can install the development version of Patterns from github with:
devtools::install_github("fbertran/Patterns")Import Cascade Data (repeated measurements on several subjects) from the CascadeData package and turn them into a omics array object. The second line makes sure the CascadeData package is installed.
library(Patterns)if(!require(CascadeData)){install.packages("CascadeData")}
data(micro_US)
micro_US<-as.omics_array(micro_US[1:100,],time=c(60,90,210,390),subject=6)
str(micro_US)
#> Formal class 'omics_array' [package "Patterns"] with 7 slots
#> ..@ omicsarray: num [1:100, 1:24] 103.2 26 70.7 213.7 13.7 ...
#> .. ..- attr(*, "dimnames")=List of 2
#> .. .. ..$ : chr [1:100] "1007_s_at" "1053_at" "117_at" "121_at" ...
#> .. .. ..$ : chr [1:24] "N1_US_T60" "N1_US_T90" "N1_US_T210" "N1_US_T390" ...
#> ..@ name : chr [1:100] "1007_s_at" "1053_at" "117_at" "121_at" ...
#> ..@ gene_ID : num 0
#> ..@ group : num 0
#> ..@ start_time: num 0
#> ..@ time : num [1:4] 60 90 210 390
#> ..@ subject : num 6Get a summay and plots of the data:
summary(micro_US)
#> N1_US_T60 N1_US_T90 N1_US_T210 N1_US_T390
#> Min. : 12.2 Min. : 12.9 Min. : 1.5 Min. : 10.1
#> 1st Qu.: 177.7 1st Qu.: 198.7 1st Qu.: 189.0 1st Qu.: 196.7
#> Median : 513.0 Median : 499.4 Median : 608.5 Median : 541.2
#> Mean :1386.6 Mean :1357.7 Mean :1450.4 Mean :1331.2
#> 3rd Qu.:1912.3 3rd Qu.:1883.4 3rd Qu.:2050.2 3rd Qu.:1646.2
#> Max. :6348.4 Max. :6507.3 Max. :6438.5 Max. :6351.4
#> N2_US_T60 N2_US_T90 N2_US_T210 N2_US_T390
#> Min. : 16.7 Min. : 3.4 Min. : 5.5 Min. : 6.1
#> 1st Qu.: 212.4 1st Qu.: 185.7 1st Qu.: 214.7 1st Qu.: 230.1
#> Median : 584.1 Median : 501.5 Median : 596.0 Median : 601.8
#> Mean :1381.9 Mean :1345.4 Mean :1410.5 Mean :1403.7
#> 3rd Qu.:1616.2 3rd Qu.:1830.5 3rd Qu.:2005.8 3rd Qu.:1901.7
#> Max. :6149.3 Max. :6090.8 Max. :6160.6 Max. :6143.1
#> N3_US_T60 N3_US_T90 N3_US_T210 N3_US_T390
#> Min. : 1.9 Min. : 10.3 Min. : 3.3 Min. : 6.6
#> 1st Qu.: 187.4 1st Qu.: 194.6 1st Qu.: 177.8 1st Qu.: 222.6
#> Median : 611.4 Median : 576.2 Median : 552.2 Median : 593.7
#> Mean :1365.4 Mean :1381.2 Mean :1310.1 Mean :1427.1
#> 3rd Qu.:1855.2 3rd Qu.:2040.2 3rd Qu.:1784.5 3rd Qu.:2131.7
#> Max. :6636.6 Max. :6515.5 Max. :6530.4 Max. :6177.2
#> N4_US_T60 N4_US_T90 N4_US_T210 N4_US_T390
#> Min. : 20.2 Min. : 15.6 Min. : 19.8 Min. : 9.3
#> 1st Qu.: 199.3 1st Qu.: 215.4 1st Qu.: 207.0 1st Qu.: 197.8
#> Median : 610.8 Median : 614.0 Median : 544.9 Median : 590.7
#> Mean :1505.1 Mean :1526.7 Mean :1401.6 Mean :1458.8
#> 3rd Qu.:2198.1 3rd Qu.:2168.9 3rd Qu.:1831.2 3rd Qu.:1984.8
#> Max. :6986.2 Max. :7148.0 Max. :6820.0 Max. :6762.3
#> N5_US_T60 N5_US_T90 N5_US_T210 N5_US_T390
#> Min. : 3.4 Min. : 10.0 Min. : 10.7 Min. : 16.5
#> 1st Qu.: 213.2 1st Qu.: 209.8 1st Qu.: 202.0 1st Qu.: 208.2
#> Median : 609.4 Median : 561.3 Median : 555.6 Median : 570.5
#> Mean :1498.2 Mean :1424.8 Mean :1394.1 Mean :1435.3
#> 3rd Qu.:2008.7 3rd Qu.:1906.5 3rd Qu.:1923.9 3rd Qu.:1867.8
#> Max. :7268.2 Max. :6857.8 Max. :6574.0 Max. :6896.6
#> N6_US_T60 N6_US_T90 N6_US_T210 N6_US_T390
#> Min. : 13.0 Min. : 6.6 Min. : 3.8 Min. : 14.4
#> 1st Qu.: 207.5 1st Qu.: 198.6 1st Qu.: 203.9 1st Qu.: 195.8
#> Median : 516.2 Median : 530.6 Median : 578.0 Median : 580.0
#> Mean :1412.9 Mean :1388.3 Mean :1416.5 Mean :1360.8
#> 3rd Qu.:2037.4 3rd Qu.:1889.8 3rd Qu.:2030.8 3rd Qu.:1872.6
#> Max. :6898.1 Max. :6749.4 Max. :6490.0 Max. :6780.2


plot(micro_US)
There are several functions to carry out gene selection before the inference. They are detailed in the vignette of the package.
Let’s simulate some cascade data and then do some reverse engineering.
We first design the F matrix for \(T_i=4\) times and \(Ngrp=4\) groups. The
Fmatobject is an array of sizes \((T_i,T-i,Ngrp^2)=(4,4,16)\).
Ti<-4
Ngrp<-4
Fmat=array(0,dim=c(Ti,Ti,Ngrp^2))
for(i in 1:(Ti^2)){
if(((i-1) %% Ti) > (i-1) %/% Ti){
Fmat[,,i][outer(1:Ti,1:Ti,function(x,y){0<(x-y) & (x-y)<2})]<-1
}
}The Patterns function CascadeFinit is an
utility function to easily define such an F matrix.
Fbis=Patterns::CascadeFinit(Ti,Ngrp,low.trig=FALSE)
str(Fbis)
#> num [1:4, 1:4, 1:16] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...Check if the two matrices Fmat and Fbis are
identical.
print(all(Fmat==Fbis))
#> [1] TRUEEnd of F matrix definition.
Fmat[,,3]<-Fmat[,,3]*0.2
Fmat[3,1,3]<-1
Fmat[4,2,3]<-1
Fmat[,,4]<-Fmat[,,3]*0.3
Fmat[4,1,4]<-1
Fmat[,,8]<-Fmat[,,3]We set the seed to make the results reproducible and draw a scale free random network.
set.seed(1)
Net<-Patterns::network_random(
nb=100,
time_label=rep(1:4,each=25),
exp=1,
init=1,
regul=round(rexp(100,1))+1,
min_expr=0.1,
max_expr=2,
casc.level=0.4
)
Net@F<-Fmat
str(Net)
#> Formal class 'omics_network' [package "Patterns"] with 6 slots
#> ..@ omics_network: num [1:100, 1:100] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
#> ..@ name : chr [1:100] "gene 1" "gene 2" "gene 3" "gene 4" ...
#> ..@ F : num [1:4, 1:4, 1:16] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
#> ..@ convF : num [1, 1] 0
#> ..@ convO : num 0
#> ..@ time_pt : int [1:4] 1 2 3 4Plot the simulated network.
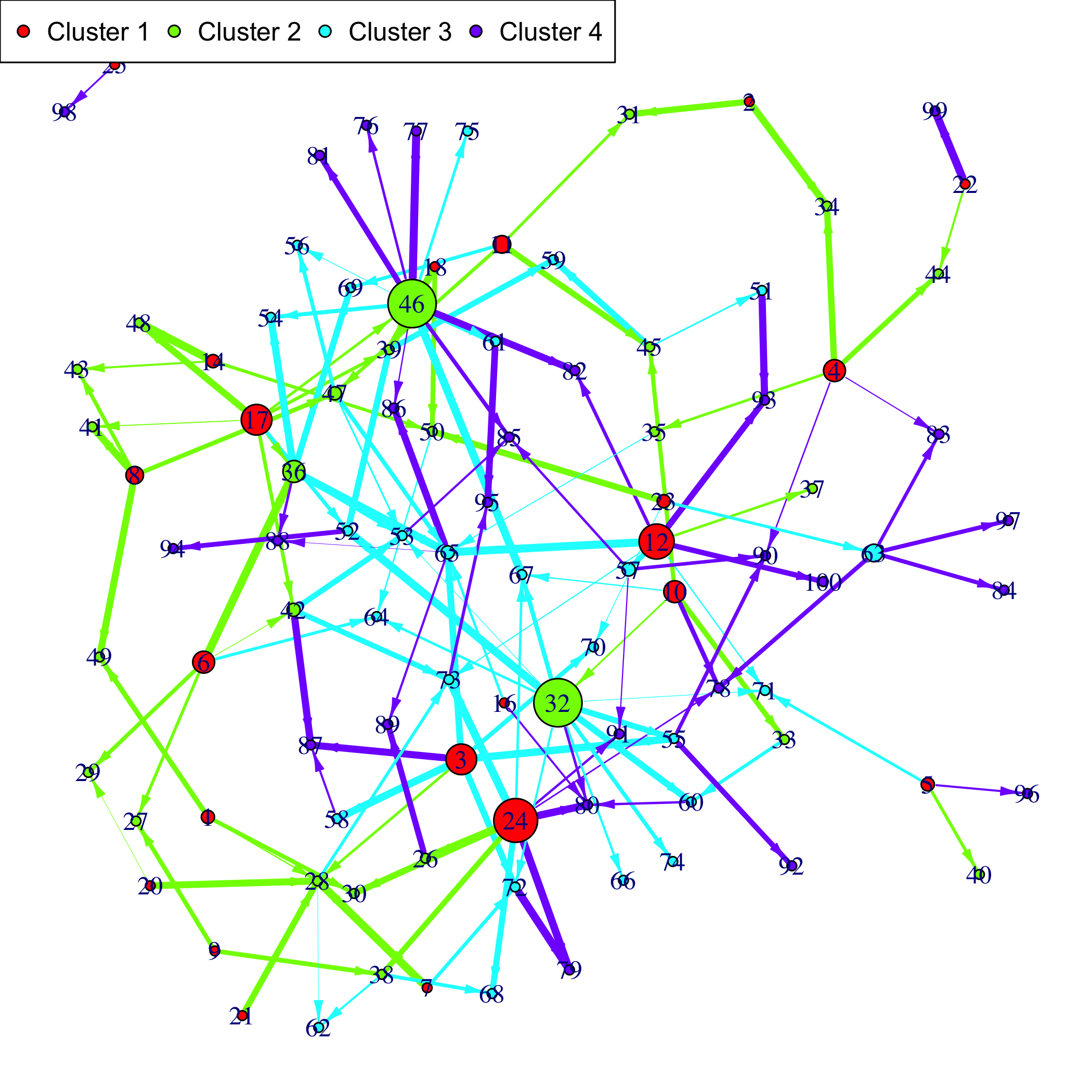
Patterns::plot(Net, choice="network")If a gene clustering is known, it can be used as a coloring scheme.
plot(Net, choice="network", gr=rep(1:4,each=25))Plot the F matrix, for low dimensional F matrices.
plot(Net, choice="F")
plot of chunk plotF
Plot the F matrix using the pixmap package, for high
dimensional F matrices.
plot(Net, choice="Fpixmap")
plot of chunk plotFpixmap
We simulate gene expression according to the network that was previously drawn
set.seed(1)
M <- Patterns::gene_expr_simulation(
network=Net,
time_label=rep(1:4,each=25),
subject=5,
peak_level=200,
act_time_group=1:4)
#> Error: unable to find an inherited method for function 'gene_expr_simulation' for signature 'omics_network = "missing"'
str(M)
#> num [1:60, 1:6] -1.495 0.368 0.517 -0.484 0.675 ...Get a summay and plots of the simulated data:
summary(M)
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'object' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'summary' : objet 'M' introuvableplot(M)
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'x' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'plot' : objet 'M' introuvableWe infer the new network using subjectwise leave one out cross-validation (default setting): all measurements from the same subject are removed from the dataset). The inference is carried out with a general Fshape.
Net_inf_P <- Patterns::inference(M, cv.subjects=TRUE)
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvablePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P' not foundHeatmap of the inferred coefficients of the Omega matrix
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P' not foundDefault values fot the \(F\)
matrices. The Finit matrix (starting values for the
algorithm). In our case, the Finitobject is an array of
sizes \((T_i,T-i,Ngrp^2)=(4,4,16)\).
Ti<-4;
ngrp<-4
nF<-ngrp^2
Finit<-array(0,c(Ti,Ti,nF))
for(ii in 1:nF){
if((ii%%(ngrp+1))==1){
Finit[,,ii]<-0
} else {
Finit[,,ii]<-cbind(rbind(rep(0,Ti-1),diag(1,Ti-1)),rep(0,Ti))+rbind(cbind(rep(0,Ti-1),diag(1,Ti-1)),rep(0,Ti))
}
}The Fshape matrix (default shape for F
matrix the algorithm). Any interaction between groups and times are
permitted except the retro-actions (a group on itself, or an action at
the same time for an actor on another one).
Fshape<-array("0",c(Ti,Ti,nF))
for(ii in 1:nF){
if((ii%%(ngrp+1))==1){
Fshape[,,ii]<-"0"
} else {
lchars <- paste("a",1:(2*Ti-1),sep="")
tempFshape<-matrix("0",Ti,Ti)
for(bb in (-Ti+1):(Ti-1)){
tempFshape<-replaceUp(tempFshape,matrix(lchars[bb+Ti],Ti,Ti),-bb)
}
tempFshape <- replaceBand(tempFshape,matrix("0",Ti,Ti),0)
Fshape[,,ii]<-tempFshape
}
}Any other form can be used. A “0” coefficient is missing from the model. It allows testing the best structure of an “F” matrix and even performing some significance tests of hypothses on the structure of the \(F\) matrix.
The IndicFshape function allows to design custom F
matrix for cascade networks with equally spaced measurements by
specifying the zero and non zero \(F_{ij}\) cells of the \(F\) matrix. It is useful for models
featuring several clusters of actors that are activated at the time.
Let’s define the following indicatrix matrix (action of all groups on
each other, which is not a possible real modeling setting and is only
used as an example):
TestIndic=matrix(!((1:(Ti^2))%%(ngrp+1)==1),byrow=TRUE,ngrp,ngrp)
TestIndic
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE
#> [2,] TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE
#> [3,] TRUE TRUE FALSE TRUE
#> [4,] TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSEFor that choice, we get those init and shape \(F\) matrices.
IndicFinit(Ti,ngrp,TestIndic)
#> , , 1
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 0 0 0 0
#> [3,] 0 0 0 0
#> [4,] 0 0 0 0
#>
#> , , 2
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 3
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 4
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 5
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 6
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 0 0 0 0
#> [3,] 0 0 0 0
#> [4,] 0 0 0 0
#>
#> , , 7
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 8
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 9
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 10
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 11
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 0 0 0 0
#> [3,] 0 0 0 0
#> [4,] 0 0 0 0
#>
#> , , 12
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 13
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 14
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 15
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0 0
#> [3,] 1 1 0 0
#> [4,] 1 1 1 0
#>
#> , , 16
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] 0 0 0 0
#> [2,] 0 0 0 0
#> [3,] 0 0 0 0
#> [4,] 0 0 0 0
IndicFshape(Ti,ngrp,TestIndic)
#> , , 1
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#>
#> , , 2
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 3
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 4
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 5
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 6
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#>
#> , , 7
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 8
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 9
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 10
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 11
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#>
#> , , 12
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 13
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 14
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 15
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "a1" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "a2" "a1" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "a3" "a2" "a1" "0"
#>
#> , , 16
#>
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
#> [1,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [2,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [3,] "0" "0" "0" "0"
#> [4,] "0" "0" "0" "0"Those \(F\) matrices are lower diagonal ones to enforce that an observed value at a given time can only be predicted by a value that was observed in the past only (i.e. neither at the same moment or in the future).
The plotF is convenient to display F matrices. Here are
the the displays of the three \(F\)
matrices we have just introduced.
plotF(Fshape,choice="Fshape")
plot of chunk plotfshape1
plotF(CascadeFshape(4,4),choice="Fshape")
plot of chunk plotfshape2
plotF(IndicFshape(Ti,ngrp,TestIndic),choice="Fshape")
plot of chunk plotfshape3
We now fit the model with an \(F\) matrix that is designed for cascade networks.
Specific Fshape
Net_inf_P_S <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4))
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvablePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_S, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_S' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network. They reflect the use of a special \(F\) matrix. It is an example of an F matrix specifically designed to deal with cascade networks.
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_S@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_S' not foundThere are many fitting functions provided with the
Patterns package in order to search for specific
features for the inferred network such as
sparsity, robust links, high
confidence links or stable through resampling
links. :
lars packageglmnet package. An
unweighted and a weighted version of the algorithm are availablespls packageelasticnet
packagec060 package
implementation of stability selectionc060 package implementation of stability selectionlars package
with light random Gaussian noise added to the explanatory variablesselectboost package implementation of the selectboost
algorithm to look for the more stable links against resampling that
takes into account the correlated structure of the predictors. If no
weights are provided, equal weigths are for all the variables (=non
weighted case).Net_inf_P_Lasso2 <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4), fitfun="LASSO2")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvablePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_Lasso2, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_Lasso2' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_Lasso2@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_Lasso2' not foundWe create a weighting vector to perform weighted lasso inference.
Weights_Net=slot(Net,"network")
#> Error in slot(Net, "network"): no slot of name "network" for this object of class "omics_network"
Weights_Net[Net@network!=0]=.1
#> Error: object 'Weights_Net' not found
Weights_Net[Net@network==0]=1000
#> Error: object 'Weights_Net' not foundNet_inf_P_Lasso2_Weighted <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4), fitfun="LASSO2", priors=Weights_Net)
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvablePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_Lasso2_Weighted, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_Lasso2_Weighted' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_Lasso2_Weighted@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_Lasso2_Weighted' not foundNet_inf_P_SPLS <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4), fitfun="SPLS")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvablePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_SPLS, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_SPLS' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_SPLS@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_SPLS' not foundNet_inf_P_ELASTICNET <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4), fitfun="ELASTICNET")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvablePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_ELASTICNET, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_ELASTICNET' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_ELASTICNET@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_ELASTICNET' not foundNet_inf_P_stability <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4), fitfun="stability.c060")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvablePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_stability, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_stability' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_stability@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_stability' not foundNet_inf_P_StabWeight <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4), fitfun="stability.c060.weighted", priors=Weights_Net)
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvablePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_StabWeight, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_StabWeight' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_StabWeight@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_StabWeight' not foundNet_inf_P_Robust <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4), fitfun="robust")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvablePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_Robust, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_Robust' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_Robust@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_Robust' not foundWeights_Net_1 <- Weights_Net
#> Error in eval(expr, envir, enclos): objet 'Weights_Net' introuvable
Weights_Net_1[,] <- 1
#> Error in Weights_Net_1[, ] <- 1: objet 'Weights_Net_1' introuvable
Net_inf_P_SelectBoost <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4), fitfun="selectboost.weighted",priors=Weights_Net_1)
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvable#>
#> Attaching package: 'Patterns'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:testthat':
#>
#> compare
#> The following object is masked from 'package:igraph':
#>
#> comparePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_SelectBoost, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_SelectBoost' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_SelectBoost@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_SelectBoost' not foundNet_inf_P_SelectBoostWeighted <- Patterns::inference(M, Finit=CascadeFinit(4,4), Fshape=CascadeFshape(4,4), fitfun="selectboost.weighted",priors=Weights_Net)
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): erreur d'�valuation de l'argument 'M' lors de la s�lection d'une m�thode pour la fonction 'inference' : objet 'M' introuvable#>
#> Attaching package: 'Patterns'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:testthat':
#>
#> compare
#> The following object is masked from 'package:igraph':
#>
#> comparePlot of the inferred F matrix
plot(Net_inf_P_SelectBoostWeighted, choice="F")
#> Error in h(simpleError(msg, call)): error in evaluating the argument 'x' in selecting a method for function 'plot': object 'Net_inf_P_SelectBoostWeighted' not foundHeatmap of the coefficients of the Omega matrix of the network
stats::heatmap(Net_inf_P_SelectBoostWeighted@network, Rowv = NA, Colv = NA, scale="none", revC=TRUE)
#> Error: object 'Net_inf_P_SelectBoostWeighted' not foundSuch an analysis is only required if the model was not fitted using the stability selection or the selectboost algorithm.
Create an animation of the network with increasing cutoffs with an animated .gif format or a html webpage in the working directory.
data(network)
sequence<-seq(0,0.2,length.out=20)
evolution(network,sequence,type.ani = "gif", outdir=getwd())
evolution(network,sequence,type.ani = "html", outdir=getwd())#> Error in setwd(outdir): cannot change working directory
#> Error in setwd(outdir): cannot change working directory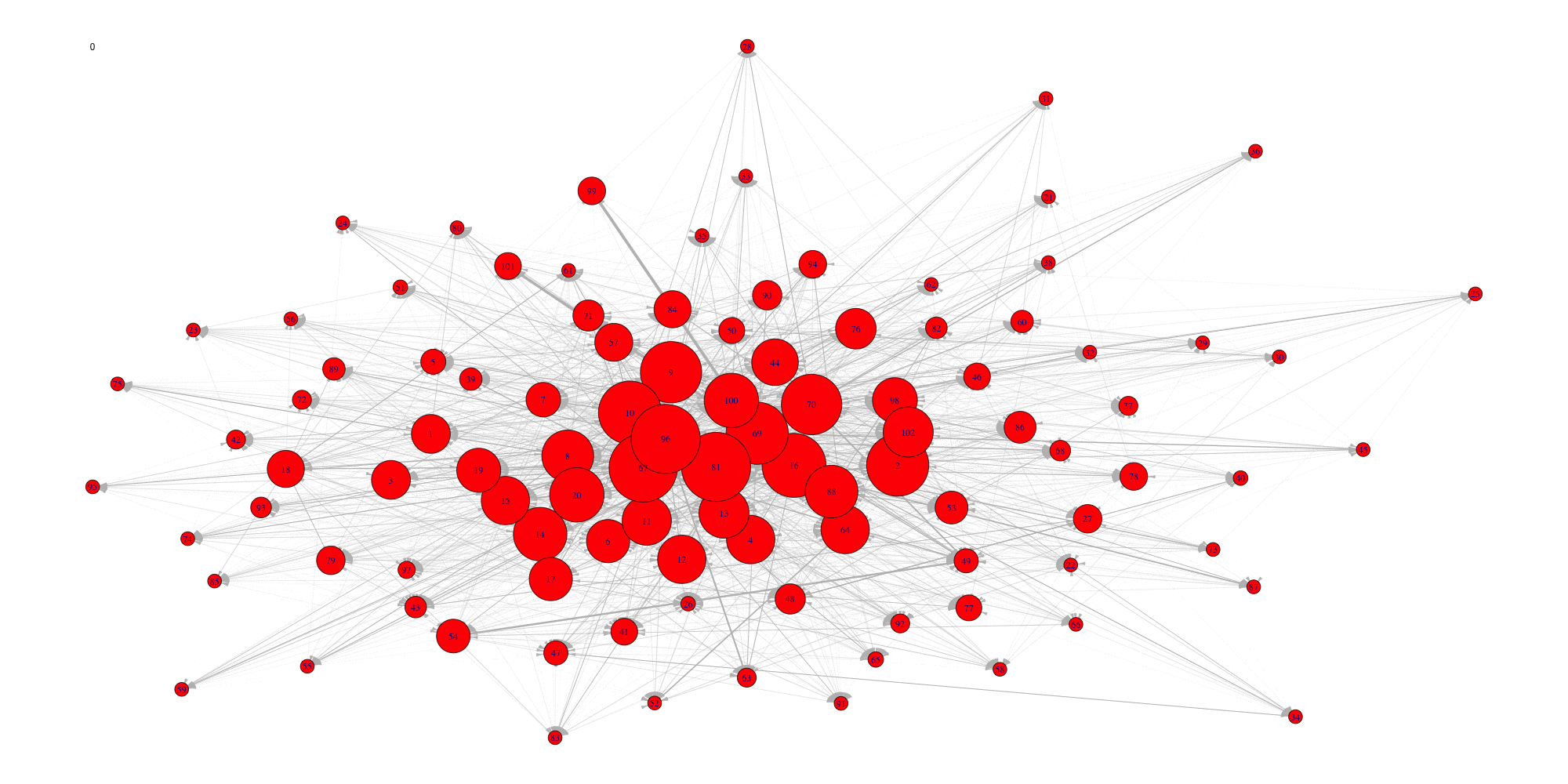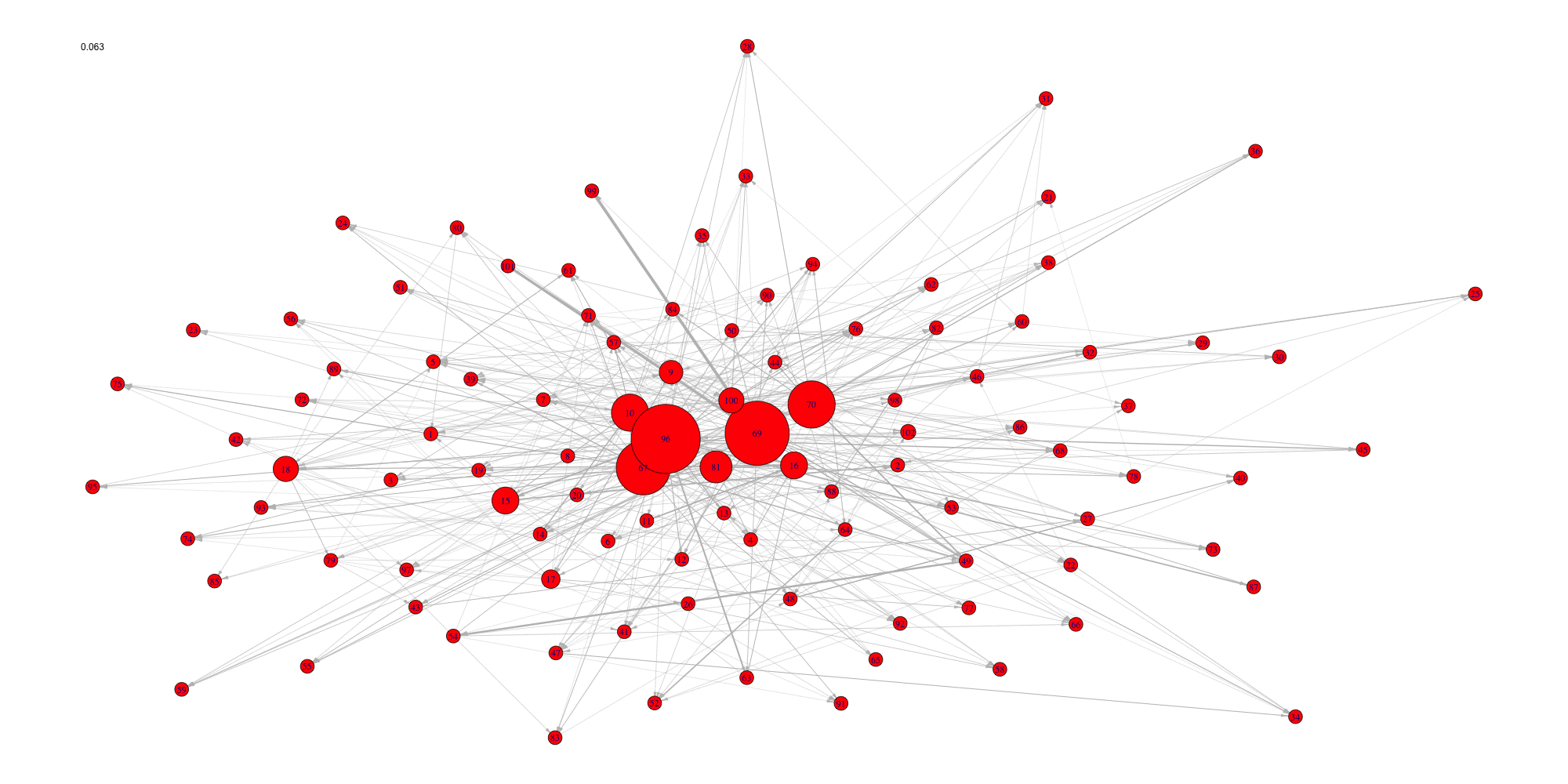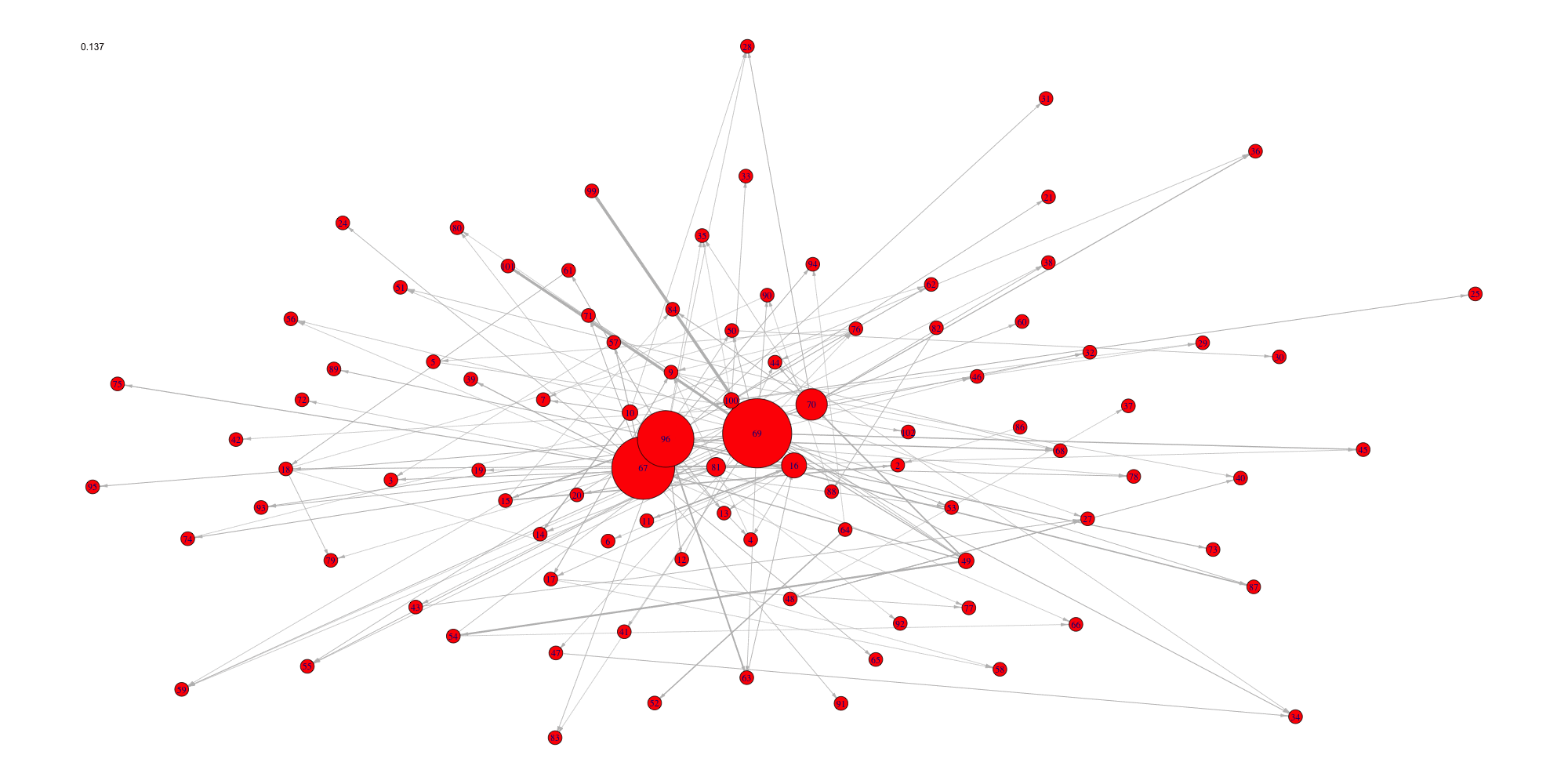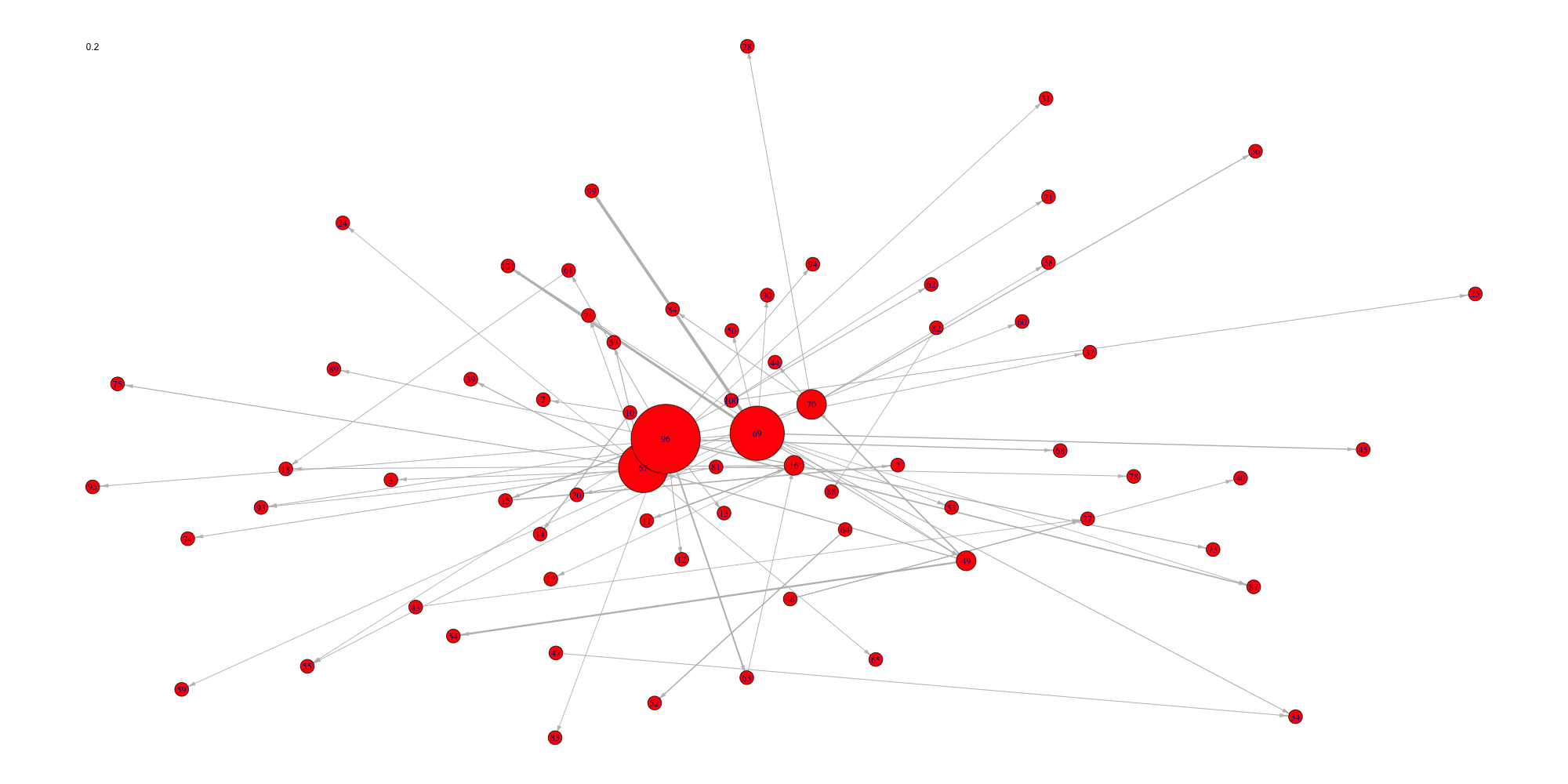
Evolution of some properties of a reverse-engineered network with
increasing cut-off values. 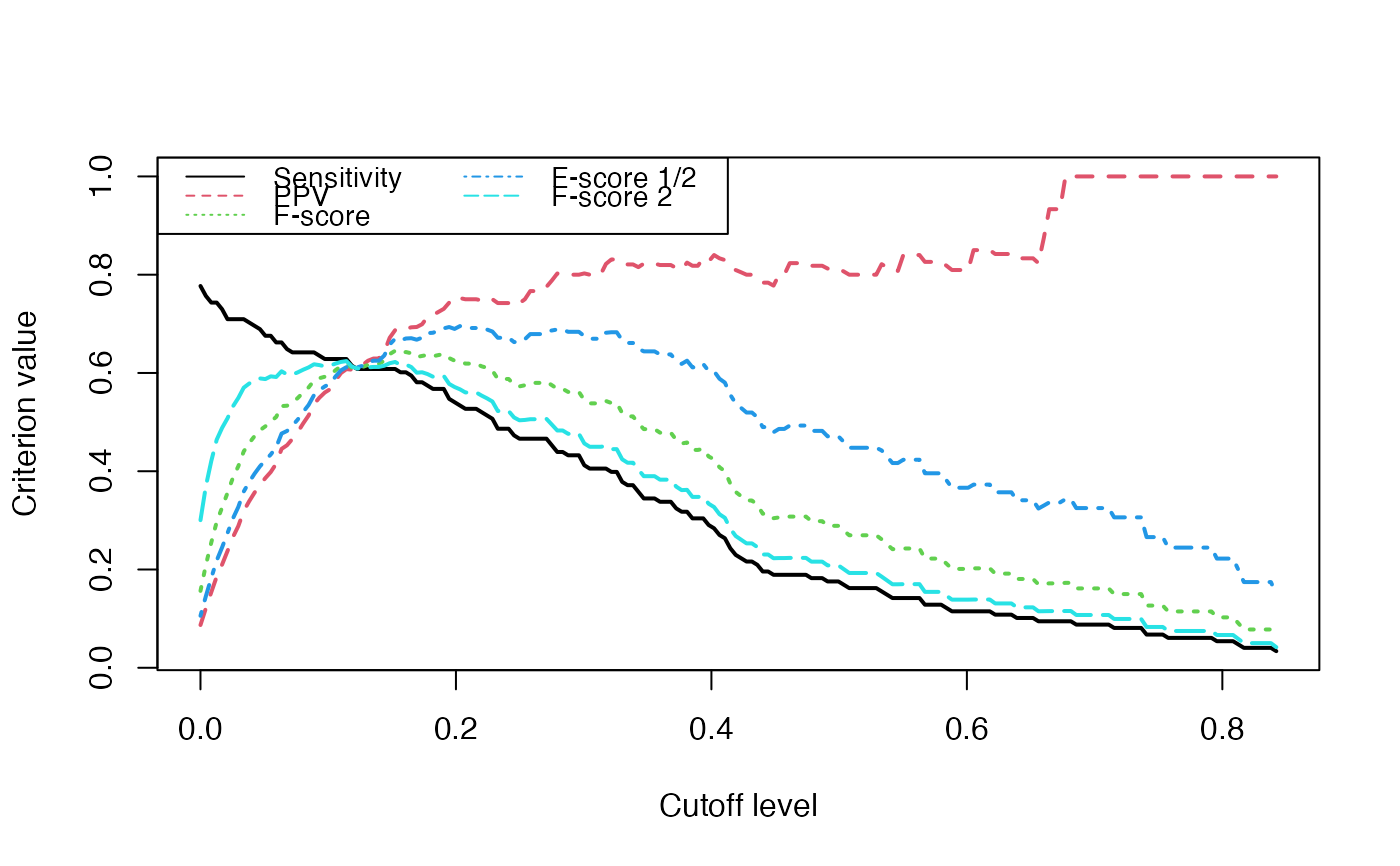
We switch to data that were derived from the inferrence of a real
biological network and try to detect the optimal cutoff value: the best
cutoff value for a network to fit a scale free network. The
cutoff was validated only single group cascade networks
(number of actors groups = number of timepoints) and for genes dataset.
Instead of the cutoff function, manual curation or the
stability selection or the selectboost algorithm should be used.
data("networkCascade")
set.seed(1)
cutoff(networkCascade)
#> Error in (function (classes, fdef, mtable) : impossible de trouver une méthode héritée pour la fonction 'cutoff' pour la signature '"network"'Analyze the network with a cutoff set to the previouly found 0.133 optimal value.
analyze_network(networkCascade,nv=0.133)
#> Error in (function (classes, fdef, mtable) : impossible de trouver une méthode héritée pour la fonction 'analyze_network' pour la signature '"network"'data(Selection)
plot(networkCascade,nv=0.133, gr=Selection@group)
plot of chunk plotnet
Import data.
library(Patterns)
library(CascadeData)
data(micro_S)
micro_S<-as.omics_array(micro_S,time=c(60,90,210,390),subject=6,gene_ID=rownames(micro_S))
data(micro_US)
micro_US<-as.omics_array(micro_US,time=c(60,90,210,390),subject=6,gene_ID=rownames(micro_US))Select early genes (t1 or t2):
Selection1<-geneSelection(x=micro_S,y=micro_US,20,wanted.patterns=rbind(c(0,1,0,0),c(1,0,0,0),c(1,1,0,0)))Section genes with first significant differential expression at t1:
Selection2<-geneSelection(x=micro_S,y=micro_US,20,peak=1)Section genes with first significant differential expression at t2:
Selection3<-geneSelection(x=micro_S,y=micro_US,20,peak=2)Select later genes (t3 or t4)
Selection4<-geneSelection(x=micro_S,y=micro_US,50,
wanted.patterns=rbind(c(0,0,1,0),c(0,0,0,1),c(1,1,0,0)))Merge those selections:
Selection<-unionOmics(Selection1,Selection2)
Selection<-unionOmics(Selection,Selection3)
Selection<-unionOmics(Selection,Selection4)
head(Selection)
#> $omicsarray
#> US60 US90 US210
#> 210226_at 0.82417544 0.9166931 0.7310784
#> 233516_s_at -0.27395188 -2.3695246 0.6511830
#> 202081_at 0.60477249 0.6599672 -0.1884742
#> 236719_at -2.07284086 -0.3123747 0.1792494
#> 236019_at -0.08175065 -0.3699708 -0.4315901
#> 1563563_at -1.44513486 1.6869516 -0.4297297
#>
#> $name
#> [1] "210226_at" "233516_s_at" "202081_at" "236719_at" "236019_at" "1563563_at"
#>
#> $gene_ID
#> [1] "210226_at" "233516_s_at" "202081_at" "236719_at" "236019_at" "1563563_at"
#>
#> $group
#> [1] 1 2 1 1 1 1
#>
#> $start_time
#> [1] 1 2 1 1 1 1
#>
#> $time
#> [1] 60 90 210 390
#>
#> $subject
#> [1] 6Summarize the final selection:
summary(Selection)
#> US60 US90 US210 US390
#> Min. :-2.76841 Min. :-2.369525 Min. :-1.6147 Min. :-2.60480
#> 1st Qu.:-0.18028 1st Qu.:-0.181425 1st Qu.: 0.1985 1st Qu.:-0.03884
#> Median : 0.05675 Median :-0.001924 Median : 0.9886 Median : 0.31766
#> Mean : 0.05764 Mean : 0.278275 Mean : 0.9611 Mean : 0.26428
#> 3rd Qu.: 0.22438 3rd Qu.: 0.664063 3rd Qu.: 1.6918 3rd Qu.: 0.57117
#> Max. : 2.86440 Max. : 4.284675 Max. : 3.6727 Max. : 2.54704
#> US60 US90 US210 US390
#> Min. :-2.7932 Min. :-2.49245 Min. :-1.21606 Min. :-1.74407
#> 1st Qu.:-0.5547 1st Qu.:-0.01944 1st Qu.: 0.07967 1st Qu.:-0.26548
#> Median :-0.3089 Median : 0.14977 Median : 0.72019 Median : 0.03616
#> Mean :-0.2917 Mean : 0.33720 Mean : 0.73063 Mean : 0.06753
#> 3rd Qu.:-0.1725 3rd Qu.: 0.48744 3rd Qu.: 1.26164 3rd Qu.: 0.32496
#> Max. : 2.0267 Max. : 3.37588 Max. : 3.87950 Max. : 2.83321
#> US60 US90 US210 US390
#> Min. :-2.94444 Min. :-0.9721 Min. :-1.9349 Min. :-3.8418
#> 1st Qu.:-0.23136 1st Qu.:-0.1027 1st Qu.: 0.3254 1st Qu.:-0.1592
#> Median :-0.04761 Median : 0.2548 Median : 1.2512 Median : 0.1538
#> Mean : 0.22116 Mean : 0.6479 Mean : 1.0485 Mean : 0.1219
#> 3rd Qu.: 0.33157 3rd Qu.: 1.0737 3rd Qu.: 1.8513 3rd Qu.: 0.6268
#> Max. : 3.31723 Max. : 4.3604 Max. : 4.4860 Max. : 1.9886
#> US60 US90 US210 US390
#> Min. :-2.85438 Min. :-0.90355 Min. :-0.83324 Min. :-0.96834
#> 1st Qu.:-0.06031 1st Qu.:-0.08464 1st Qu.: 0.07605 1st Qu.: 0.01569
#> Median : 0.03601 Median : 0.17135 Median : 0.52176 Median : 0.17370
#> Mean : 0.14593 Mean : 0.41929 Mean : 0.62446 Mean : 0.23854
#> 3rd Qu.: 0.24568 3rd Qu.: 0.75564 3rd Qu.: 1.07821 3rd Qu.: 0.45189
#> Max. : 1.82903 Max. : 3.60640 Max. : 2.27744 Max. : 1.90880
#> US60 US90 US210 US390
#> Min. :-1.38002 Min. :-2.94444 Min. :-1.0271 Min. :-1.3636
#> 1st Qu.:-0.19910 1st Qu.:-0.01758 1st Qu.: 0.1459 1st Qu.:-0.1386
#> Median :-0.07962 Median : 0.16080 Median : 0.7430 Median : 0.1492
#> Mean : 0.12972 Mean : 0.37123 Mean : 0.7972 Mean : 0.1271
#> 3rd Qu.: 0.26113 3rd Qu.: 0.61933 3rd Qu.: 1.3922 3rd Qu.: 0.4825
#> Max. : 2.31074 Max. : 3.24454 Max. : 3.6213 Max. : 1.5979
#> US60 US90 US210 US390
#> Min. :-1.79176 Min. :-3.20791 Min. :-1.4716 Min. :-1.95883
#> 1st Qu.:-0.09822 1st Qu.:-0.03963 1st Qu.: 0.1292 1st Qu.:-0.04786
#> Median : 0.03378 Median : 0.28261 Median : 0.8392 Median : 0.22472
#> Mean : 0.27978 Mean : 0.52529 Mean : 0.7903 Mean : 0.21171
#> 3rd Qu.: 0.33548 3rd Qu.: 1.03256 3rd Qu.: 1.4416 3rd Qu.: 0.42511
#> Max. : 3.16035 Max. : 3.19975 Max. : 2.8027 Max. : 2.14903
plot of chunk omicsselection6

plot of chunk omicsselection6

plot of chunk omicsselection6
Plot the final selection:
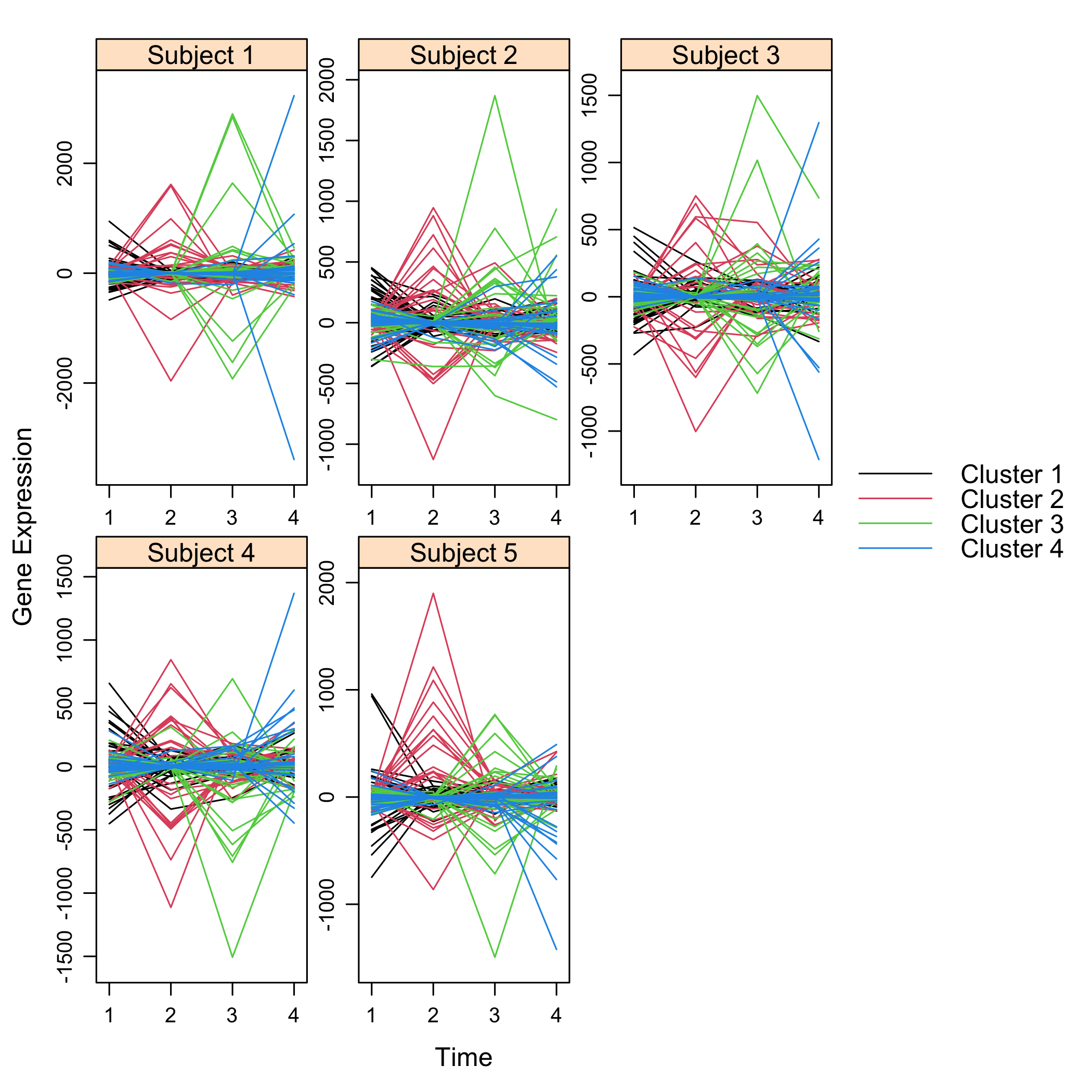
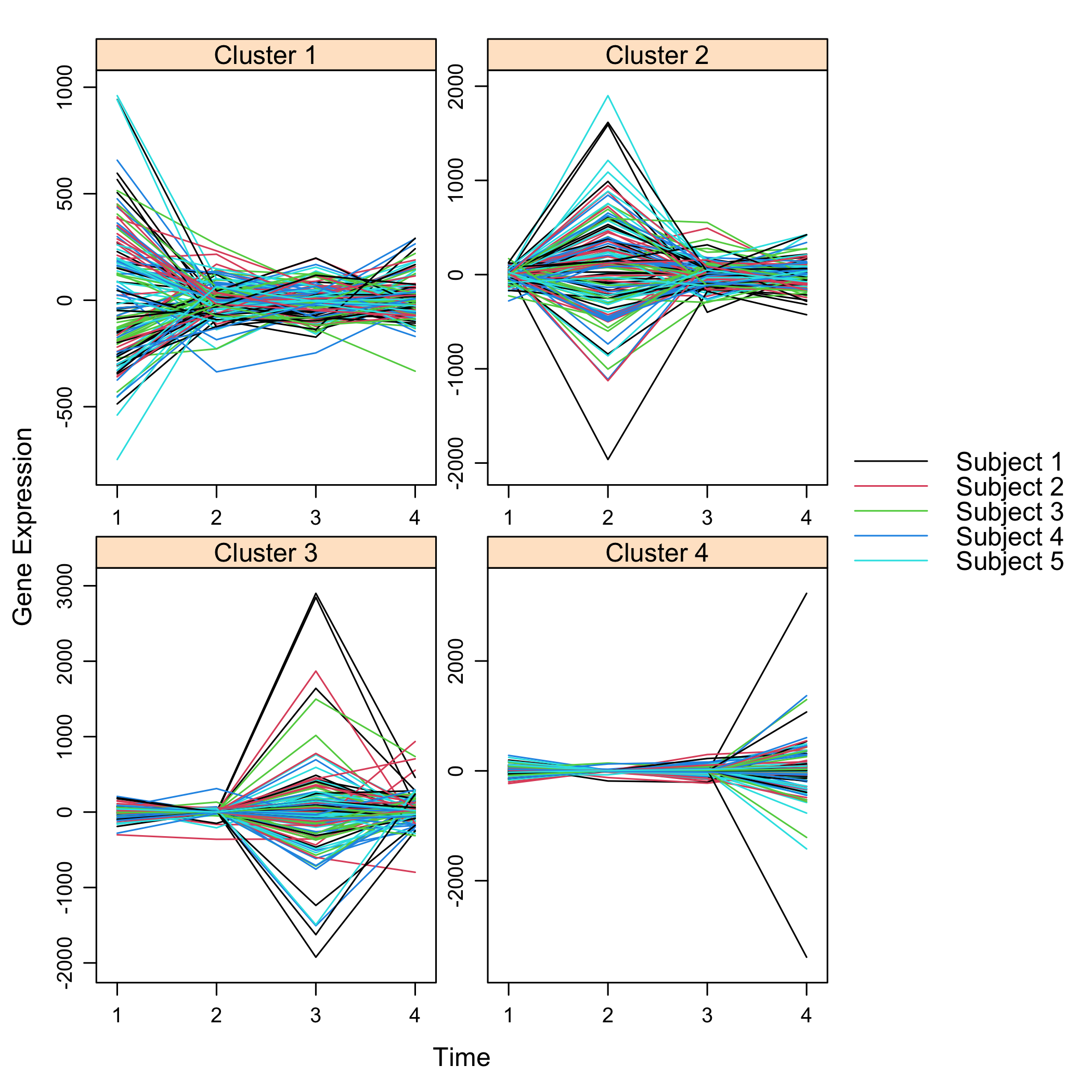
plot(Selection)
plot of chunk omicsselection7

plot of chunk omicsselection7

plot of chunk omicsselection7

plot of chunk omicsselection7

plot of chunk omicsselection7

plot of chunk omicsselection7

plot of chunk omicsselection7

plot of chunk omicsselection7
This process could be improved by retrieve a real gene_ID using the
bitr function of the ClusterProfiler package
or by performing independent filtering using jetset package
to only keep at most only probeset (the best one, if there is one good
enough) per gene_ID.



These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.