
The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by METANET, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]metanet.ch.

The asymptor R package allows you to estimate the lower and upper bound of asymptomatic cases in an epidemic using the capture/recapture methods from Böhning et al. (2020) and Rocchetti et al. (2020).
Please note there is currently some discussion about the validity of the methods implemented in this package. You should read carefully the original articles, alongside this answer from Li et al. (2022) before using this package in your project.
You can install the stable version of this package from CRAN:
install.packages("asymptor")or the development version from GitHub, via my r-universe:
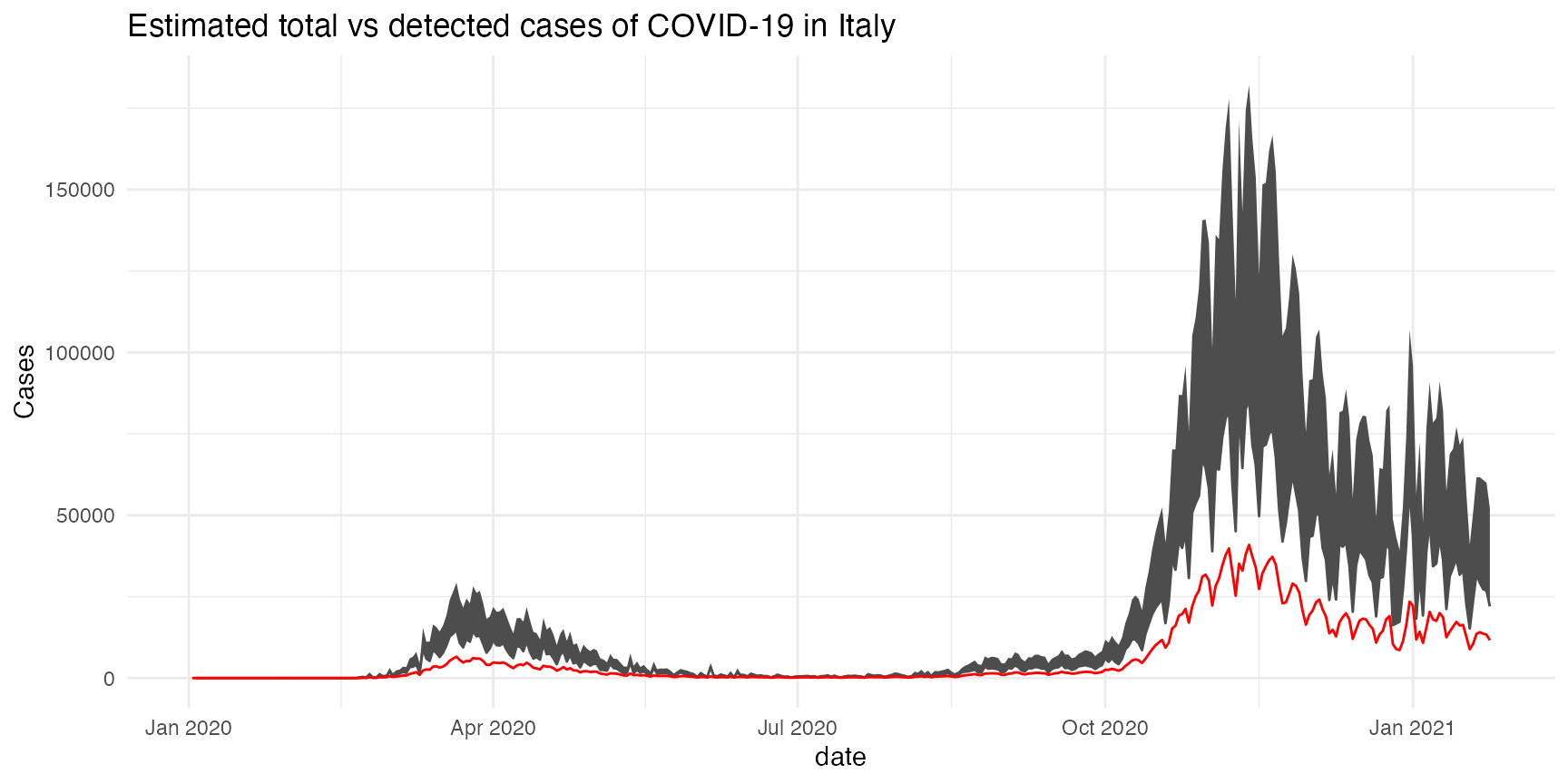
install.packages("asymptor", repos = "https://bisaloo.r-universe.dev")Let’s start by loading some example data from the COVID-19 epidemic in Italy:
d <- readRDS(system.file("extdata", "covid19_italy.rds", package = "asymptor"))
head(d)
#> date new_cases new_deaths
#> 1 2020-01-02 0 0
#> 2 2020-01-03 0 0
#> 3 2020-01-04 0 0
#> 4 2020-01-05 0 0
#> 5 2020-01-06 0 0
#> 6 2020-01-07 0 0We can estimate the lower and upper bound of asymptomatic cases with:
library(asymptor)
estimate_asympto(d$date, d$new_cases, d$new_deaths)Or, with a tidyverse-compatible syntax:
library(dplyr)
d %>%
mutate(asympto_cases = estimate_asympto(date, new_cases, new_deaths))Please refer to the vignette for a detailed example using the COVID-19 data from Italy.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.