The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by METANET, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]metanet.ch.
Publication: https://peerj.com/articles/6398/
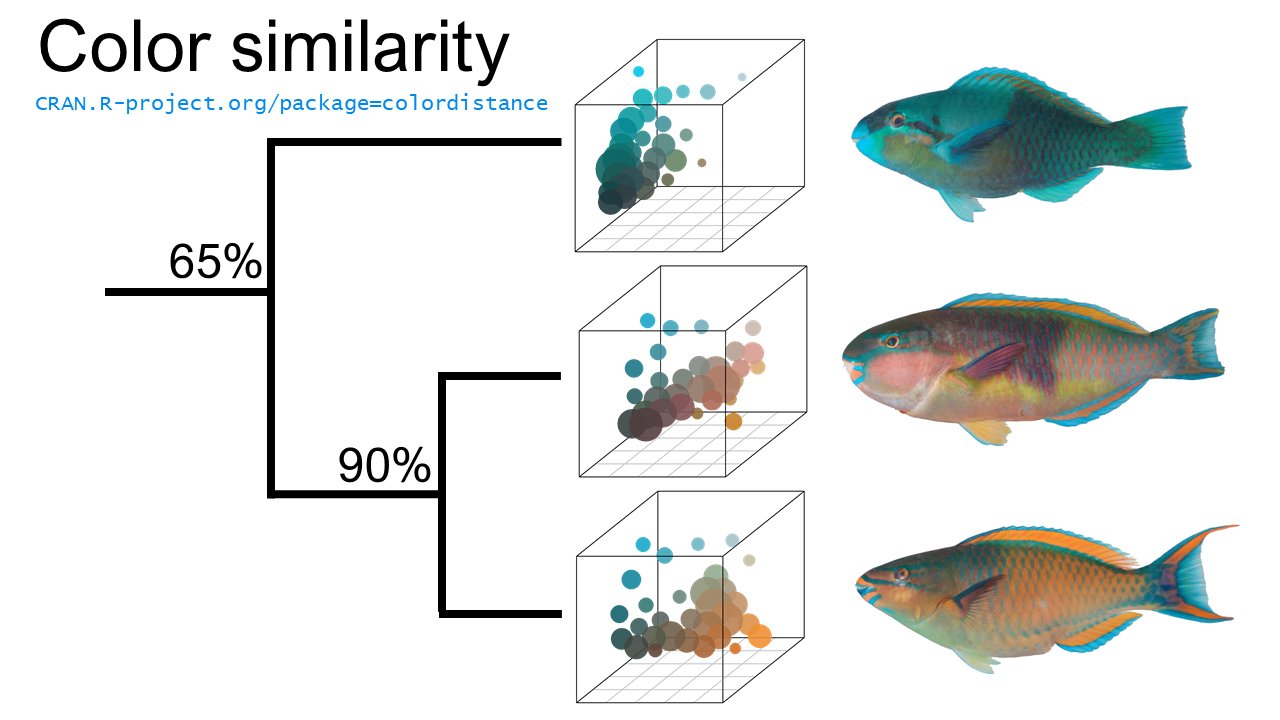
An R package with functions for quantifying the differences between colorful objects. Loads and displays images, selectively masks specified background colors, bins pixels by color using either data-dependent or automatically generated color bins, quantitatively measures color similarity among images using one of several distance metrics for comparing pixel color clusters, and clusters images by object color similarity. Originally written for use with organism coloration (reef fish color diversity, butterfly mimicry, etc), but easily applicable for any image set.
March 18, 2021: Minor updates to do with
spatstat package (a sub-package,
spatstat.geom, is now required instead). This shouldn’t
affect installation or usage.
November 11, 2020: Transparencies (alpha channel)
can now be used to mask image backgrounds. By default, the presence of
transparent pixels in a PNG overrides other background parameters, and
the transparent pixels are ignored as background. This behavior can be
disabled by setting alpha.channel = FALSE in any function
that takes an image path as an argument. This allows users to specify
the background in an image without having to decide on a background
color that is sufficiently different from the object of interest.
Backgrounds of uniform color can easily be rendered transparent using
Photoshop, ImageJ, or GIMP.
February 19, 2020: Thanks to Evelyn Taylor-Cox for
pointing out a bug with getLabHist when specifying
a.bounds and b.bounds, resulting in bins that
did not sum to 1. The bug should now be fixed in the development
version!
February 6, 2019: Our methods paper for
colordistance is out in PeerJ! Find it here: https://peerj.com/articles/6398/.
December 27, 2018: Fixed a bug when converting color clusters using convertColorSpace.
July 10, 2018: Added scatter3dclusters
function to plot clusters in color space, scaled according to their size
and colored according to their color. This is helpful for visualizing
the distributions that colordistance actually compares to
come up with a distance matrix, since the histograms can give the
misleading impression that the clusters are treated as one-dimensional
after binning. Also tweaked some compatibilities.
June 26, 2018: Added option to perform analyses CIELAB color space, as well as warnings about perceptual non-uniformity of RGB space. RGB (with warning) is still the default in order to prompt users to read up on CIELAB before using it. See “Color Spaces” and “CIELab Analyses” vignettes.
April 19, 2018: Functions for combining data across
a set of images (combineClusters and
combineList) added. Useful for pooling multiple images of
the same individual, species, etc before analysis.
Input: Set(s) of JPEG or PNG images of colorful objects, optionally with backgrounds masked out.
Output: Color clusters, visualizations for color binning and image similarity, and distance matrices quantifying color similarity between images.
Requirements: R >= 3.3.2
Documentation: https://hiweller.github.io/colordistance/
Author: Hannah Weller
Contact: hannahiweller@gmail.com
The development version of colordistance can be found at
https://github.com/hiweller/colordistance.
To install the development version of colordistance in
R:
Install the devtools package
(install.packages("devtools")).
Install colordistance without vignettes
(long-form documentation) to save time and space or with
vignettes for offline access to help documents.
# Without vignettes
devtools::install_github("hiweller/colordistance")
# With vignettes
devtools::install_github("hiweller/colordistance", build_vignettes=TRUE)You can access help documents by running
help(package="colordistance") and clicking on the html
files or, if you set build_vignettes=TRUE during install,
run vignette("colordistance-introduction").
To install the stable release version on CRAN
(https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=colordistance), just run
install.packages("colordistance").
All of the colordistance vignettes that (optionally)
come with the package are also available online at https://hiweller.github.io/colordistance/. I recommend
reading at least the introduction before getting started.
To get started with colordistance, you’ll need:
A set of images of objects you want to compare, ideally as
consistent with each other as possible in terms of lighting and angle,
and with anything you want to ignore masked
out with a uniform background color. Need something to get started?
Try these
butterflyfish photos! colordistance also comes with an
example set of Heliconius butterfly pictures from Meyer,
2006, which you can access via
system.file("extdata", "Heliconius", package="colordistance")
in R.
R version 3.3.2 or later.
Estimates for the upper and lower RGB bounds for your background
color. R reads in pixels channels with a 0-1 intensity range instead of
the typical 0-255 (so pure red would be [1, 0, 0], green would be [0, 1,
0], blue would be [0, 0, 1], and so on). Background masking is rarely
perfect, so you’ll need to specify an upper and lower threshold for the
background cutoff - around 0.2 usually does it. So if your background is
white, your lower threshold would be [0.8, 0.8, 0.8] and your upper
would be [1, 1, 1]. The default background color for
colordistance is bright green, [0, 1, 0].
To run an analysis with all the default settings (bright green background masking, RGB color histograms with 3 bins per channel, and earth mover’s distance for color distance metric – see documentation), just run:
colordistance::imageClusterPipeline("path/to/images/folder")You’ll get a blue and yellow heatmap with a cluster dendrogram and
labels taken from the image names. Yellow cells correspond to
dissimilar images; blue cells correspond to more
similar images. If those scores don’t look right, try changing
the number of bins (bins argument), the distance metric
(distanceMethod argument), and making sure you’re masking
out the right background color.
colordistanceOur methods paper describing colordistance is now out in PeerJ! Please cite
the package as: Weller HI, Westneat MW. 2019. Quantitative color
profiling of digital images with earth mover’s distance using the R
package colordistance. PeerJ 7:e6398
https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6398
If something is wrong or confusing, or if you’d like to see a change, please create an issue on the issues page of the GitHub repository, as it allows other people to see it. You can also email me at hannahiweller@gmail.com.
If you would like to contribute, feel free to make a pull request or email me with your thoughts.
Email me at hannahiweller@gmail.com. I generally respond within 48 hours.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.