| Type: | Package |
| Title: | Generate Generative Data for a Data Source |
| Version: | 2.1.6 |
| Date: | 2025-12-16 |
| Author: | Werner Mueller [aut, cre] |
| Maintainer: | Werner Mueller <werner.mueller5@chello.at> |
| Description: | Generative Adversarial Networks are applied to generate generative data for a data source. A generative model consisting of a generator and a discriminator network is trained. During iterative training the distribution of generated data is converging to that of the data source. Direct applications of generative data are the created functions for data evaluation, missing data completion and data classification. A software service for accelerated training of generative models on graphics processing units is available. Reference: Goodfellow et al. (2014) <doi:10.48550/arXiv.1406.2661>. |
| License: | GPL-2 | GPL-3 [expanded from: GPL (≥ 2)] |
| Imports: | Rcpp (≥ 1.0.3), tensorflow (≥ 2.0.0), httr (≥ 1.4.7) |
| LinkingTo: | Rcpp |
| RoxygenNote: | 7.3.3 |
| SystemRequirements: | TensorFlow (https://www.tensorflow.org) |
| NeedsCompilation: | yes |
| Encoding: | UTF-8 |
| Packaged: | 2025-12-16 22:02:45 UTC; ubuntu |
| Repository: | CRAN |
| Date/Publication: | 2025-12-16 22:20:02 UTC |
Generate generative data for a data source
Description
Generative Adversarial Networks are applied to generate generative data for a data source. A generative model consisting of a generator and a discriminator network is trained. During iterative training the distribution of generated data is converging to that of the data source.
Generated data can be written to a file in training and after finished training in a separate generation step. First method accumulates generative data using a dynamic model, second method generates generative data using a static model.
Inserted images show two-dimensional projections of generative data for the iris dataset:
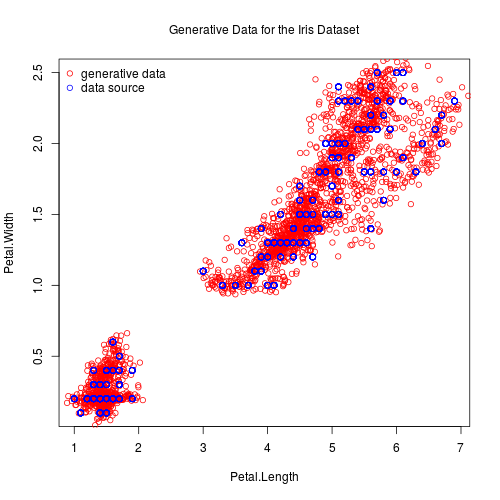
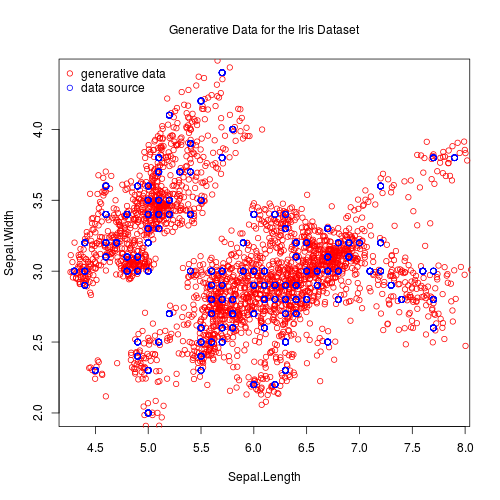
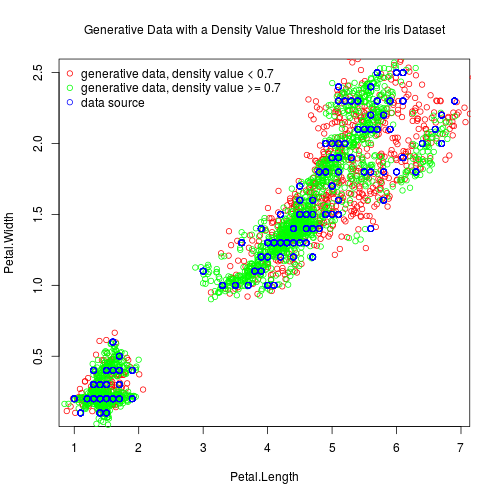
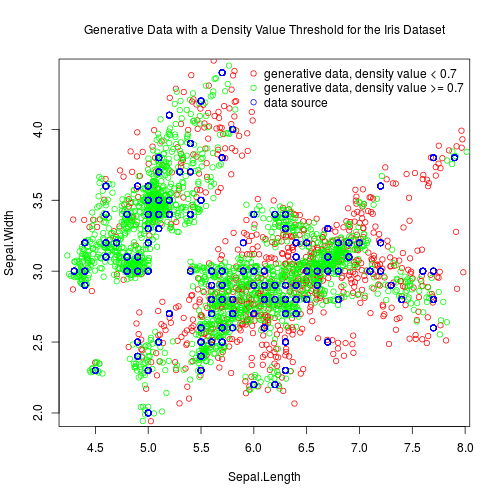
Details
The API includes functions for topics "definition of data source" and "generation of generative data". Main function of first topic is dsCreateWithDataFrame() which creates a data source with passed data frame. Main functions of second topic are gdTrain() which trains a generative model for a data source and gdGenerate() which uses a trained generative model to generate generative data. Additionally a software service for accelerated training of generative models is available.
1. Definition of data source
dsCreateWithDataFrame() Create a data source with passed data frame.
dsActivateColumns() Activate columns in a data source in order to include them in training of generative models.
By default columns are active.
dsDeactivateColumns() Deactivate columns in a data source in order to exclude them from training of generative models.
Note that the training function in the package supports only columns of type R-class numeric, R-type double.
All columns of other type have to be deactivated.
The training function in the software service for accelerated training of generative models supports columns of any type.
dsGetActiveColumnNames() Get names of active columns of a data source.
dsGetInactiveColumnNames() Get names of inactive columns of a data source.
dsWrite() Write created data source including settings of active columns to a file in binary format. This file will be used as input in functions of topic "generation of generative data".
dsRead() Read a data source from a file that was written with dsWrite().
dsGetNumberOfRows() Get number of rows in a data source.
dsGetRow() Get a row in a data source.
dsCalculateDensityValues() Read a data souce from a file, calculate density values and write the data source with density values to original file.
dsDensityValueInverseQuantile() Calculate inverse density value quantile for a density value.
2. Training of generative model and generation of generative data
gdTrainParameters() Specify parameters for training of generative model.
gdTrain() Read a data source from a file, train a generative model that generates generative data for the data source in iterative training steps, write trained generative model and generated data in training steps to a file in binary format..
gdGenerateParameters() Specify parameters for generation of generative data.
gdGenerate() Read a generative model and a data source from a file, generate generative data for the data source and write generated data to a file in binary format.
gdCalculateDensityValues() Read generative data from a file, calculate density values and write generative data with density values to original file.
gdRead() Read generative data and data source from specified files.
gdPlotParameters() Specify plot parameters for generative data.
gdPlotDataSourceParameters() Specify plot parameters for data source.
gdPlotProjection() Create an image file containing two-dimensional projections of generative data and data source.
gdGetNumberOfRows() Get number of rows in generative data.
gdGetRow() Get a row in generative data.
gdCalculateDensityValue() Calculate density value for a data record.
gdDensityValueQuantile() Calculate density value quantile for a percent value.
gdDensityValueInverseQuantile() Calculate inverse density value quantile for a density value.
gdKNearestNeighbors() Search for k nearest neighbors in generative data.
gdComplete() Complete incomplete data record.
gdWriteSubset() Write subset of generative data.
3. Software service for accelerated training of generative models
gdServiceTrain() Send a request to software service to train a generative model.
gdServiceGetGenerativeData() Get generated generative data from software service.
gdServiceGetGenerativeModel() Get trained generative model from software service.
gdServiveGetStatus() Get status of generated job from software service.
gdServiceDelete() Delete generated job from software service.
Author(s)
Werner Mueller
Maintainer: Werner Mueller <werner.mueller5@chello.at>
References
Ian J. Goodfellow, Jean Pouget-Abadie, Mehdi Mirza, Bing Xu, David Warde-Farley, Sherjil Ozair, Aaron Courville, Yoshua Bengio (2014), "Generative Adversarial Nets", <arXiv:1406.2661v1>
Examples
# Environment used for execution of examples:
# Operating system: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS
# Compiler: g++ 13.3.0 (supports C++17 standard)
# Software: Python 3.12.3, TensorFlow 2.16.2
# R environment: R 4.5.2, RStudio 2024.12.1
# Installed packages: 'Rcpp' 1.1.0, 'tensorflow' 2.20.0,
# 'ganGenerativeData' 2.1.5
# Package 'tensorflow' provides an interface to machine learning framework
# TensorFlow. To complete the installation function install_tensorflow() has to
# be called.
## Not run:
library(tensorflow)
install_tensorflow()
## End(Not run)
# Generate generative data for the iris dataset
# Load library
library(ganGenerativeData)
# 1. Definition of data source for the iris dataset
# Create a data source with iris data frame.
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
# Deactivate the column with name Species and index 5 in order to exclude it in
# trainng of generative model.
dsDeactivateColumns(c(5))
# Get the active column names: Sepal.Length, Sepal.Width, Petal.Length,
# Petal.Width.
dsGetActiveColumnNames()
# Write the data source including settings of active columns to file
# "ds.bin" in binary format.
## Not run:
dsWrite("ds.bin")
## End(Not run)
# 2. Training of generative model and generation of generative data for the iris
# data source
# Read data source from file "ds.bin", train a generative model in iterative
# training steps (used number of iterations in tests is in the range of 10000 to
# 50000), write trained generative model and generated data in training steps to
# files "gm.bin" and "gd.bin".
## Not run:
gdTrain("gm.bin", "gd.bin", "ds.bin", c(1, 2),
gdTrainParameters(numberOfTrainingIterations = 1000))
## End(Not run)
# Read generative data from file "gd.bin", calculate density values and
# write generative data with density values to original file.
## Not run:
gdCalculateDensityValues("gd.bin")
## End(Not run)
# Read generative data from file "gd.bin" and data source from "ds.bin". Read in
# data will be accessed in following function calls.
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin", "ds.bin")
## End(Not run)
# Create an image showing two-dimensional projections of generative data and
# data source for column indices 3, 4 and write it to file "gd34d.png".
## Not run:
gdPlotProjection("gd34d.png",
"Generative Data for the Iris Dataset",
c(3, 4),
gdPlotParameters(50),
gdPlotDataSourceParameters(100))
## End(Not run)
# Create an image showing two-dimensional projections of generative data and
# data source for column indices 3, 4 with density value threshold 0.71 and
# write it to file "gd34ddv.png".
## Not run:
gdPlotProjection("gd34ddv.png",
"Generative Data with a Density Value Threshold for the Iris Dataset",
c(3, 4),
gdPlotParameters(50, c(0.38), c("red", "green")),
gdPlotDataSourceParameters(100))
## End(Not run)
# Get number of rows in generative data
## Not run:
gdGetNumberOfRows()
## End(Not run)
# Get row with index 1000 in generative data
## Not run:
gdGetRow(1000)
## End(Not run)
# Calculate density value for a data record
## Not run:
gdCalculateDensityValue(list(6.1, 2.6, 5.6, 1.4))
## End(Not run)
# Calculate density value quantile for 50 percent
## Not run:
gdDensityValueQuantile(50)
## End(Not run)
# Calculate inverse density value quantile for density value 0.5
## Not run:
gdDensityValueInverseQuantile(0.5)
## End(Not run)
# Search for k nearest neighbors for a data record
## Not run:
gdKNearestNeighbors(list(5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2), 3)
## End(Not run)
# Complete incomplete data record containing an NA value
## Not run:
gdComplete(list(5.1, 3.5, 1.4, NA))
## End(Not run)
# Write subset containing 50 percent of randomly selected rows of
# generative data
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin")
gdWriteSubset("gds.bin", 50)
## End(Not run)
# 3. Usage of software service for accelerated training of a generative
# model
# Initialize variables for URL and access key.
## Not run:
url <- "http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/gdService"
accessKey <- "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
## End(Not run)
# Send a request to software service to train a generative model for a data
# source. A job id will be returned.
## Not run:
trainParameters <- gdTrainParameters(numberOfTrainingIterations = 10000,
numberOfInitializationIterations = 2500)
jobId <- gdServiceTrain(url, accessKey, "gmService.bin", "gdService.bin", "ds.bin",
trainParameters)
## End(Not run)
# Get status of generated job from software service. When job is processed
# successfully status will be set to TRAINED.
## Not run:
gdServiceGetStatus(url, accessKey, jobId)
## End(Not run)
# Get generated generative data from software service for processed job
## Not run:
gdServiceGetGenerativeData(url, accessKey, jobId, "gdService.bin")
## End(Not run)
# Get trained generative model from software service for processed job
## Not run:
gdServiceGetGenerativeModel(url, accessKey, jobId, "gmService.bin")
## End(Not run)
Activate columns
Description
Activate columns in a data source in order to include them in training of generative models. By default columns are active.
Usage
dsActivateColumns(columnVector)
Arguments
columnVector |
Vector of column indices |
Value
None
Examples
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
dsGetActiveColumnNames()
dsDeactivateColumns(c(5))
dsGetActiveColumnNames()
dsActivateColumns(c(5))
dsGetActiveColumnNames()
Calculate density values for data source
Description
Read a data source from a file, calculate density values and write the data source with density values to original file. Calculated density values are used to evaluate a data source.
Usage
dsCalculateDensityValues(dataSourceFileName, nNearestNeighbors)
Arguments
dataSourceFileName |
Name of data source file name |
nNearestNeighbors |
number of used nearest neighbors |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
dsCalculateDensityValues("ds.bin")
## End(Not run)
Create a data source with passed data frame
Description
Create a data source with passed data frame.
Usage
dsCreateWithDataFrame(dataFrame)
Arguments
dataFrame |
Name of data frame |
Value
None
Examples
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
Deactivate columns
Description
Deactivate columns in a data source in order to exclude them from training of generative models. Note that the training function in the package supports only columns of type R-class numeric, R-type double. All columns of other type have to be deactivated. The training function in the software service for accelerated training of generative models supports columns of any type.
Usage
dsDeactivateColumns(columnVector)
Arguments
columnVector |
Vector of column indices |
Value
None
Examples
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
dsDeactivateColumns(c(5))
dsGetInactiveColumnNames()
Calculate inverse density value quantile
Description
Calculate inverse density value quantile for a density value.
Usage
dsDensityValueInverseQuantile(densityValue)
Arguments
densityValue |
Normalized density value |
Value
Percent value
Examples
## Not run:
dsRead("ds.bin")
dsDensityValueInverseQuantile(0.5)
## End(Not run)
Get active column names
Description
Get active column names of a data source
Usage
dsGetActiveColumnNames()
Value
Vector of names of active columns
Examples
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
dsDeactivateColumns(c(5))
dsGetActiveColumnNames()
Get inactive column names
Description
Get inactive column names of a data source
Usage
dsGetInactiveColumnNames()
Value
Vector of names of inactive columns
Examples
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
dsDeactivateColumns(c(5))
dsGetInactiveColumnNames()
Get number of rows
Description
Get number of rows in a data source
Usage
dsGetNumberOfRows()
Value
Number of rows
Examples
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
dsGetNumberOfRows()
Get a row in a data source
Description
Get a row in a data source for a row index.
Usage
dsGetRow(index)
Arguments
index |
Index of row |
Value
List containing row in data source
Examples
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
dsGetRow(1)
Read a data source from file
Description
Read a data source from a file in binary format
Usage
dsRead(fileName)
Arguments
fileName |
Name of data source file |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
dsDeactivateColumns(c(5))
dsWrite("ds.bin")
dsRead("ds.bin")
## End(Not run)
Write a data source to file
Description
Write a data source including settings of active columns to a file in binary format.
This file will be used as input in functions for generation of generative data.
Usage
dsWrite(fileName)
Arguments
fileName |
Name of data source file |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
dsCreateWithDataFrame(iris)
dsDeactivateColumns(c(5))
dsWrite("ds.bin")
## End(Not run)
Calculate density value for a data record
Description
Calculate density value for a data record. By default for the calculation a linear search is performed on normalized generative data. When a search tree is used search is performed on a tree for generative data which is built once in the first function call.
Usage
gdCalculateDensityValue(dataRecord, useSearchTree = FALSE)
Arguments
dataRecord |
List containing an unnormalized data record. |
useSearchTree |
Boolean value indicating if a search tree should be used. |
Value
Normalized density value number
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin")
dv <- gdCalculateDensityValue(list(6.1, 2.6, 5.6, 1.4))
## End(Not run)
Calculate density values for generative data
Description
Read generative data from a file, calculate density values and write generative data with density values to original file. Calculated density values are used to classify generative data. In function gdPlotParameters() density value thresholds with assigned colors can be passed to draw generative data for different density value ranges.
Usage
gdCalculateDensityValues(generativeDataFileName)
Arguments
generativeDataFileName |
Name of generative data file name |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
gdCalculateDensityValues("gd.bin")
## End(Not run)
Complete incomplete data record
Description
Search for first nearest neighbor in normalized generative data for incomplete data record containing NA values. Found row in generative data is then used to replace NA values in inccomplete data record. This function calls gdKNearestNeighbors() with parameter k equal to 1.
Usage
gdComplete(dataRecord, useSearchTree = FALSE)
Arguments
dataRecord |
List containing an incomplete unnormalized data record |
useSearchTree |
Boolean value indicating if a search tree should be used. |
Value
List containing completed denormalized data record
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin")
gdComplete(list(5.1, 3.5, 1.4, NA))
## End(Not run)
Calculate inverse density value quantile
Description
Calculate inverse density value quantile for a density value.
Usage
gdDensityValueInverseQuantile(densityValue)
Arguments
densityValue |
Normalized density value |
Value
Percent value
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin")
gdDensityValueInverseQuantile(0.5)
## End(Not run)
Calculate density value quantile
Description
Calculate density value quantile for a percent value.
Usage
gdDensityValueQuantile(percent)
Arguments
percent |
Percent value |
Value
Normalized density value quantile number
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin")
gdDensityValueQuantile(50)
## End(Not run)
Generate generative data for a data source
Description
Read a trained generative model for a data source, generate generative data and write generated data to a file in binary format.
Usage
gdGenerate(
generativeDataFileName,
generativeModelFileName,
generateParameters = gdGenerateParameters(numberOfSamples = 10000, dropout = 0.05)
)
Arguments
generativeDataFileName |
Name of generative data file |
generativeModelFileName |
Name of generative model file |
generateParameters |
Generation of generative data parameters, see function gdGenerateParameters(). |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
generateParameters <- gdGenerateParameters(numberOfSamples = 10000)
gdGenerate("gd.bin", "gm.bin", generateParameters)
## End(Not run)
Specify parameters for generation of generative data
Description
Specify parameters for generation of generative data. These parameters are passed to function gdGenerate().
Usage
gdGenerateParameters(numberOfSamples = 1e+05, dropout = 0.05)
Arguments
numberOfSamples |
Number of generated samples |
dropout |
Value in the range of 0 to 1. Specifies the rate of hidden units that are dropped. Dropout is a regularization method to prevent overfitting. See function gdTrainParameters(). |
Value
List of parameters for generation of generative data
Examples
## Not run:
generateParameters <- gdGenerateParameters(numberOfSamples = 100000)
## End(Not run)
Get number of rows
Description
Get number of rows in generative data
Usage
gdGetNumberOfRows()
Value
Number of rows
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin")
gdGetNumberOfRows()
## End(Not run)
Get a row in generative data
Description
Get a row in generative data for a row index
Usage
gdGetRow(index)
Arguments
index |
Index of row |
Value
List containing a denormalized row in normalized generative data.
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin")
gdGetRow(1000)
## End(Not run)
Search for k nearest neighbors
Description
Search for k nearest neighbors in normalized generative data for a data record. When the data record contains NA values only the non-NA values are considered in search. By default a linear search is performed. When a search tree is used search is performed on a tree which is built once in the first function call. Building a tree is also triggered when NA values in data records change in subsequent function calls.
Usage
gdKNearestNeighbors(dataRecord, k = 1L, useSearchTree = FALSE)
Arguments
dataRecord |
List containing an unnormalized data record |
k |
Number of nearest neighbors |
useSearchTree |
Boolean value indicating if a search tree should be used. |
Value
A list of denormalized rows in normalized generative data
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin")
gdKNearestNeighbors(list(5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2), 3)
## End(Not run)
Specify plot parameters for data source
Description
Specify plot parameters for data source passed to function gdPlotProjection().
Usage
gdPlotDataSourceParameters(percent = 100, color = "blue")
Arguments
percent |
Percent of randomly selected rows in data source |
color |
Colour for data points of data source |
Value
List of plot parameters for data source
Examples
## Not run:
gdPlotDataSourceParameters(2500)
## End(Not run)
Specify plot parameters for generative data
Description
Specify plot parameters for generative data passed to function gdPlotProjection(). When density value thresholds with assigned colors are specified generative data is drawn for density value ranges in increasing order.
Usage
gdPlotParameters(
percent = 10,
densityValueThresholds = c(),
densityValueColors = c("red")
)
Arguments
percent |
Percent of randomly selected rows in generative data |
densityValueThresholds |
Vector of density value thresholds |
densityValueColors |
Vector of colors assigned to density value thresholds. The size must be the size of densityValueThresholds plus one. |
Value
List of plot parameters for generative data
Examples
## Not run:
gdPlotParameters(50, c(0.75), c("red", "green"))
## End(Not run)
Create an image file for generative data and data source
Description
Create an image file containing two-dimensional projections of generative data and data source. Plot pagd_2500_6.binrameters for generative data and data source are passed by functions gdPlotParameters() and gdPlotDataSourceParameters(). Data points of data source are drawn above data points of generative data.
Usage
gdPlotProjection(
imageFileName,
title,
columnIndices,
generativeDataParameters = gdPlotParameters(percent = 10, densityValueThresholds = c(),
densityValueColors = c("red")),
dataSourceParameters = gdPlotDataSourceParameters(percent = 100, color = "blue")
)
Arguments
imageFileName |
Name of image file |
title |
Title of image |
columnIndices |
Vector of two column indices that are used for the two-dimensional projections. Indices refer to indices of active columns of data source. |
generativeDataParameters |
Plot generative data parameters, see function gdPlotParameters(). |
dataSourceParameters |
Plot data source parameters, see function gdPlotDataSourceParameters(). |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin", "ds.bin")
gdPlotProjection("gd12ddv.png",
"Generative Data with a Density Value Threshold for the Iris Dataset", c(1, 2),
gdPlotParameters(250000, c(0.71), c("red", "green")),
gdPlotDataSourceParameters(2500))
gdPlotProjection("gd34ddv.png",
"Generative Data with a Densit(y Value Threshold for the Iris Dataset", c(3, 4),
gdPlotParameters(250000, c(0.71), c("red", "green")),
gdPlotDataSourceParameters(2500))
## End(Not run)
Read generative data and data source
Description
Read generative data and data source from specified files. Read in generative data and data source are accessed in gdPlot2dProjection(), generative data is accessed in gdGetRow(), gdCalculateDensityValue() and gdCalculateDensityValueQuantile().
Usage
gdRead(generativeDataFileName, dataSourceFileName = "")
Arguments
generativeDataFileName |
Name of generative data file |
dataSourceFileName |
Name of data source file |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin", "ds.bin")
## End(Not run)
Delete a generated job from software service for accelerated training of generative models
Description
Delete a generated job from software service. If the job is currently executed it it will be stopped.
Usage
gdServiceDelete(url, accessKey, jobId)
Arguments
url |
URL of software service for accelerated training of generative models |
accessKey |
Unique key for access to software service |
jobId |
Job id for generated job for training a generative model |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
url <- "http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/gdService"
accessKey <- "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
gdServiceDelete(url, accessKey, 1)
## End(Not run)
Get generative data from software service for accelerated training of generative models for processed job
Description
Download generated generative data from software service for processed job. The status of the job has to be TRAINED.
Usage
gdServiceGetGenerativeData(
url,
accessKey,
jobId,
generativeDataFileName = NULL
)
Arguments
url |
URL of software service for accelerated training of generative models |
accessKey |
Unique key for access to software service |
jobId |
Job id for generated job for training a generative model |
generativeDataFileName |
Name of generative data file. If name is NULL or empty string name of passed name to function gdServiceTrain() will be used. |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
url <- "http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/gdService"
accessKey <- "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
gdServiceGetGenerativeData(url, accessKey, 1, "gd.bin")
## End(Not run)
Get generative model from software service for accelerated training of generative models for processed job
Description
Download trained generative model from software service for processed job. The status of the job has to be TRAINED.
Usage
gdServiceGetGenerativeModel(
url,
accessKey,
jobId,
generativeModelFileName = NULL
)
Arguments
url |
URL of software service for accelerated training of generative models |
accessKey |
Unique key for access to software service |
jobId |
Job id for generated job for training a generative model |
generativeModelFileName |
Name of generative model file. If name is NULL or empty string name of passed name to function gdServiceTrain() will be used. |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
url <- "http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/gdService"
accessKey <- "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
gdServiceGetGenerativeModel(url, accessKey, 1, "gm.bin")
## End(Not run)
Get status of generated job from software service for accelerated training of generative models
Description
Get status of generated job from software service. Defined status values are: CREATED, UPLOADED, TRAINING, TRAINED, DELETED, ERROR.
Usage
gdServiceGetStatus(url, accessKey, jobId)
Arguments
url |
URL of software service for accelerated training of generative models |
accessKey |
Unique key for access to software service |
jobId |
Job id for generated job for training a generative model |
Value
List containing status information
Examples
## Not run:
url <- "http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/gdService"
accessKey <- "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
gdServiceGetStatus(url, accessKey, 1)
## End(Not run)
Send a request to software service for accelerated training of generative models to train a generative model for a data source
Description
Send a request to software service to train a generative model. A data source file will be uploaded and a job for training will be generated. A job id for the generated job will be returned which has to be used in related requests. The job will be processed as soon as other waiting jobs are processed. When a name of an existing generative model file is passed the file will be also uploaded and the job will continue the training. See also functions gdTrain(), gdServiceGetGenerativeModel(), gdServiceGetGenerativeData(), gdServiceGetStatus(), gdServiceDelete().
Usage
gdServiceTrain(
url,
accessKey,
generativeModelFileName,
generativeDataFileName,
dataSourceFileName,
trainParameters = gdTrainParameters(numberOfTrainingIterations = 10000,
numberOfInitializationIterations = 2500, numberOfHiddenLayerUnits = 1024,
learningRate = 7e-05, dropout = 0.05)
)
Arguments
url |
URL of software service for accelerated training of generative models |
accessKey |
Unique key for access to software service |
generativeModelFileName |
Name of generative model file |
generativeDataFileName |
Name of generative data file. If name is NULL or empty string generated data will not be written to a file. |
dataSourceFileName |
Name of data source file |
trainParameters |
Generative model training parameters, see function gdTrainParameters(). |
Value
Job Id number
Examples
## Not run:
url <- "http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/gdService"
accessKey <- "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
trainParameters <- gdTrainParameters(numberOfTrainingIterations = 10000)
jobId <- gdServiceTrain(url, accessKey, "gm.bin", "gd.bin", "ds.bin", trainParameters)
## End(Not run)
Train a generative model for a data source
Description
Read a data source from a file, train a generative model that generates normalized generative data for the data source in iterative training steps, write trained generative model and normalized generated data to a file in binary format. When a higher number of iterations is used the distribution of generated data will get closer to that of the data source. When a name of an existing generative model file is passed training will be continued.
Usage
gdTrain(
generativeModelFileName,
generativeDataFileName,
dataSourceFileName,
columnIndices,
trainParameters = gdTrainParameters(numberOfTrainingIterations = 10000,
numberOfInitializationIterations = 1500, numberOfHiddenLayerUnits = 1024,
learningRate = 7e-05, dropout = 0.05)
)
Arguments
generativeModelFileName |
Name of generative model file |
generativeDataFileName |
Name of generative data file. When name is NULL or empty string generated data will not be written to a file. |
dataSourceFileName |
Name of data source file |
columnIndices |
Vector of two column indices that are used to plot two-dimensional projections of normalized generated generative data and data source for a training step. Indices refer to indices of active columns of data source. Plotting can be disabled by passing NULL or an empty vector. |
trainParameters |
Generative model training parameters, see function gdTrainParameters(). |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
trainParameters <- gdTrainParameters(numberOfTrainingIterations = 10000)
gdTrain("gm.bin", "gd.bin", "ds.bin", c(1, 2), trainParameters)
## End(Not run)
Specify parameters for training of generative model
Description
Specify parameters for training of neural networks used for generation of generative data. These parameters are passed to function gdTrain().
Usage
gdTrainParameters(
numberOfTrainingIterations = 10000,
numberOfInitializationIterations = 1500,
numberOfHiddenLayerUnits = 1024,
learningRate = 7e-05,
dropout = 0.1
)
Arguments
numberOfTrainingIterations |
Number of training iterations |
numberOfInitializationIterations |
Number of initialization iterations |
numberOfHiddenLayerUnits |
Number of hidden layer units |
learningRate |
Learning rate for training of neural networks |
dropout |
Value in the range of 0 to 1. Specifies the rate of hidden units that are dropped. Dropout is a regularization method to prevent overfitting. |
Value
List of parameters for training of generative model
Examples
## Not run:
generateParameters <- gdGenerateParameters(numberOfTrainingIterations = 10000)
## End(Not run)
Write subset of generative data
Description
Write subset of randomly selected rows of generative data
Usage
gdWriteSubset(fileName, percent)
Arguments
fileName |
Name of subset generative data file |
percent |
Percent of randomly selected rows |
Value
None
Examples
## Not run:
gdRead("gd.bin")
gdWriteSubset("gds.bin", 50)
## End(Not run)