The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by METANET, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]metanet.ch.
The hillshader package is a wrapper around the
rayshader and raster packages to create
hillshade relief maps using ray-tracing, and write them to (spatial)
files.
The stable version of hillshader can be installed from
CRAN:
install.packages("hillshader")Alternatively, if you feel brave, you can install the development
version of hillshader with the remotes
package:
remotes::install_github("pierreroudier/hillshader")Below is a quick tutorial of the hillshader
capabilities:
hillshader
functionThe hillshader function is the main function of that
package, and allows to create a hillshade map as a
RasterLayer:
library(raster)
#> Loading required package: sp
library(rayshader)
library(hillshader)Note that the hillshader package includes the
maungawhau and maungawhau_hr datasets. These
are geo-referenced, raster datasets. maungawhau corresponds
to the well-known volcano dataset. It is a 87 × 61
elevation matrix for Maungawhau,
one of the circa 80 volcanoes in the Auckland volcano filed, in
Aotearoa/New Zealand. The maungawhau_hr dataset is a
“high-resolution” version of that dataset, and is a 1 m resolution,
860 × 600 elevation matrix derived from a LiDAR dataset recorded by NZ
Aerial Mapping & Aerial Surveying Limited for Auckland Council, and
distributed
by Land Information New Zealand.
layout(matrix(c(1,2), nrow = 1, ncol = 2))
image(maungawhau, asp = 1, main = "Maungawhau", col = terrain.colors(100))
image(maungawhau_hr, asp = 1, main = "Maungawhau (high-resolution)", col = terrain.colors(100))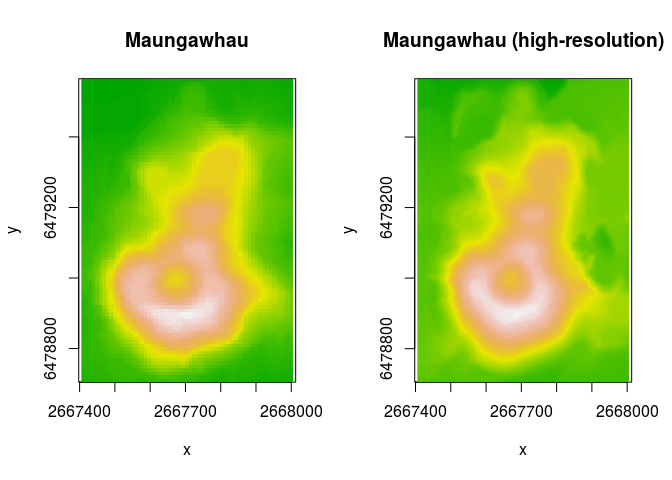
The hillshader function can be simply called on a
elevation raster to generate a hillshade RasterLayer. By
default, the shader used is rayshader::ray_shade, with its
default values.
hs <- hillshader(maungawhau_hr)
plot_map(hs)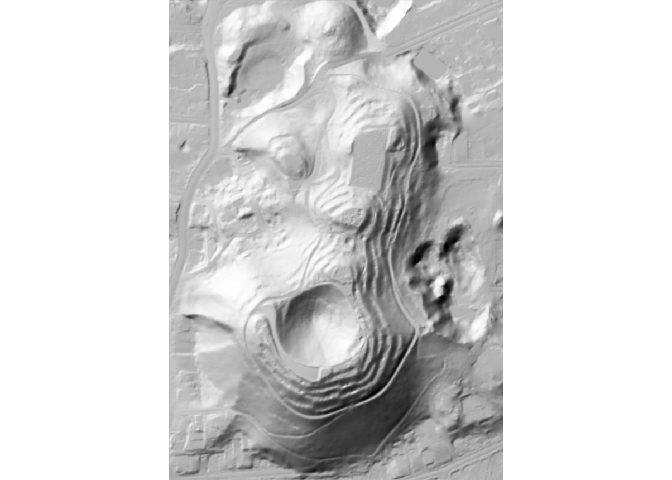
The hillshader function accept a shader
option, with is a list of the successive shader functions to apply to
create the hillshade layer. The accepted values must be
rayshader shader functions (ray_shade,
ambient_shade, lamb_shade), and the order is
important.
hs <- hillshader(
elevation = maungawhau_hr,
shader = c("ray_shade", "ambient_shade")
)
plot_map(hs)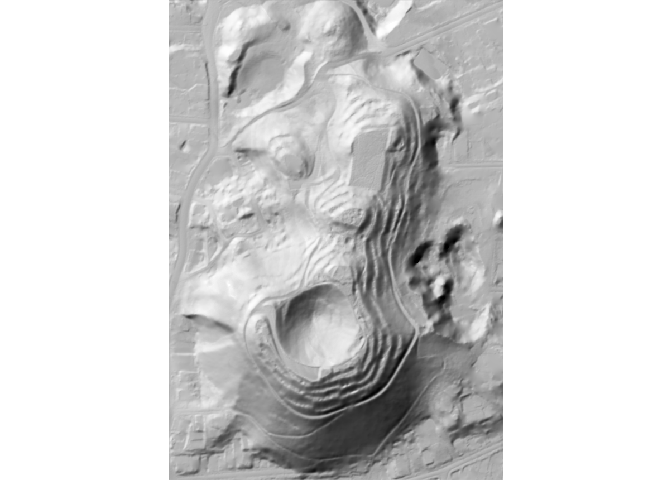
The hillshader function uses the rayshader
options defaults, but other values can be specify and passed as
arguments:
hs <- hillshader(
elevation = maungawhau_hr,
shader = c("ray_shade", "ambient_shade"),
sunangle = 180,
sunaltitude = 25
)
plot_map(hs)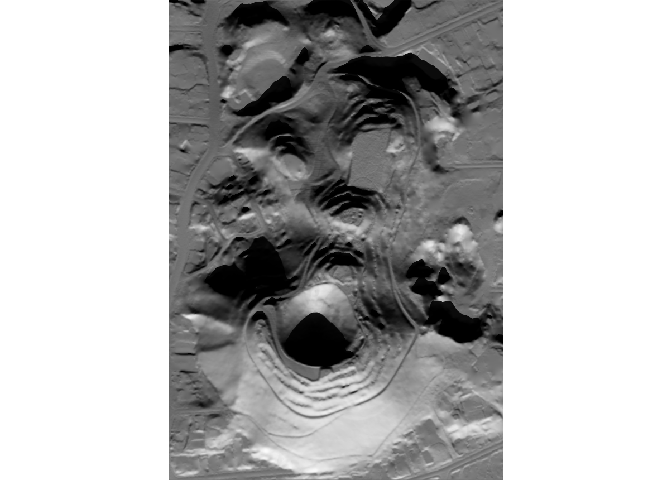
library(raster)
slope <- terrain(maungawhau_hr, out = "slope")
aspect <- terrain(maungawhau_hr, out = "aspect")
hs_raster <- hillShade(
slope,
aspect,
angle = 40,
direction = 325
)
hs_hillshader <- hillshader(
maungawhau_hr,
c("ray_shade", "ambient_shade"),
sunangle = 325,
sunaltitude = 40
)
layout(matrix(c(1,2), nrow = 1, ncol = 2))
image(hs_raster, asp = 1, main = "Classic hillshade", col = grey.colors(100))
image(hs_hillshader, asp = 1, main = "Ray-traced hillshade", col = grey.colors(100))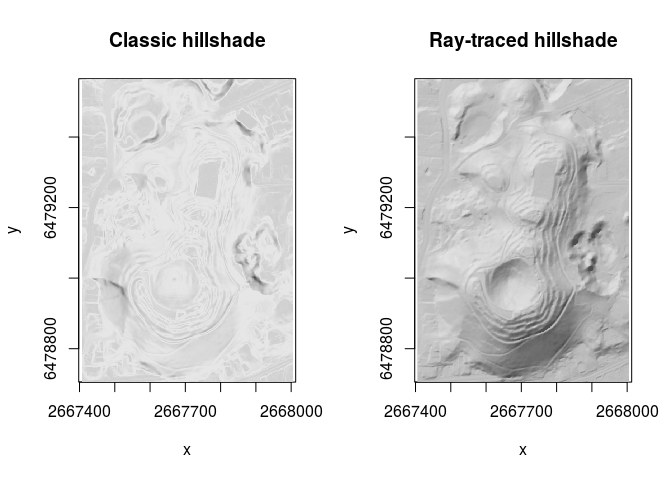
If a filename is passed to hillshader, then
the resulting hillshade layer is saved to file. This is a wrapper around
raster::writeRaster, and options specific to the latter
function can be used.
hillshader(
elevation = maungawhau_hr,
shader = c("ray_shade", "ambient_shade"),
sunangle = 180,
sunaltitude = 25,
filename = "hillshade.tif"
)rayshader pipelinesThe hillshader package provides three functions that can
be used within the rayshader pipelines:
add_shadow_2d: a function that multiplies a shadow map
by another shadow map, a corrected 2D version of
rayshader::add_shadow,matrix_to_raster: a function that converts a matrix
(typically used by the rayshader functions) back to a
RasterLayer, for input into a GIS workflow,write_raster: a function that a hillshade matrix to a
raster file format.library(rayshader)
library(hillshader)
# Create elevation matrix
el_mat <- raster_to_matrix(maungawhau_hr)
el_mat %>%
# Create hillshade layer using
# ray-tracing
ray_shade %>%
# Add ambient shading
add_shadow_2d(
ambient_shade(
heightmap = el_mat
)
) %>%
# Write to GIS file
write_raster(
elevation = maungawhau_hr,
filename = "hillshade.tif"
)Please note that the hillshader project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.