The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by METANET, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]metanet.ch.
In survival analysis, events sometimes only start to occur after a
certain delay since entry time and this delay period might vary for
different treatments or groups. While parametric delay models, like the
three-parameter Weibull distribution, might adequately describe this
process the estimation of delay via standard maximum likelihood is
severely biased in small samples. The R-package incubate
employs an alternative estimation method called maximum product of
spacings estimation (MPSE) to estimate and test delay and other
parameters in a one or two group setting. Concretely, building on MPSE,
incubate can
The incubate-package provides the delayed exponential
distribution as special case of the delayed Weibull distribution. We
draw random samples corresponding to two groups with different model
parameters.
library("incubate")
# simulate data from exponential distribution with delay
x <- rexp_delayed(n = 13, delay1 = 1.0, rate1 = 0.8)
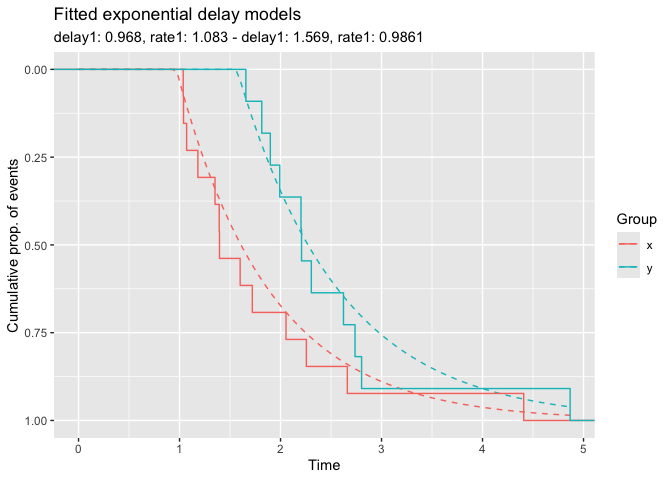
y <- rexp_delayed(n = 11, delay1 = 1.5, rate1 = 1.2)We use the model function delay_model to fit a
exponential model with delay to both groups and show the model fit.
fm <- delay_model(x, y)
plot(fm)
Inference on the model parameters is possible through
confint for bootstrap confidence intervals and
delay_test for parameter comparisons in a two group
setting.
# confidence interval for delay-parameters
confint(fm, parm = c('delay1.x', 'delay1.y'))
#> 2.5% 97.5%
#> delay1.x 0.8060324 1.094331
#> delay1.y 1.3505534 1.753090
# test on difference in delay
# for real applications use R>=1000 bootstrap draws
delay_test <- test_diff(x, y, R = 100)
plot(delay_test)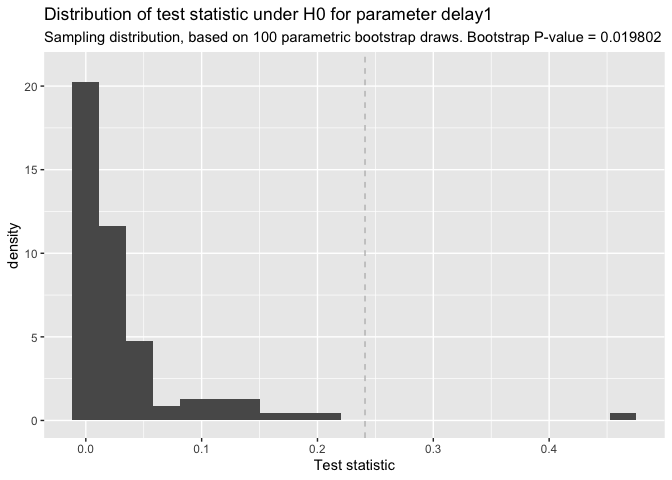
To switch on parallel computation, e.g. for bootstrap parameter tests
or power simulations, simply set up a suitable computation plan via the
Future-API. For instance, do the following to activate four R-sessions
in the background of your local computer for computer-intensive tasks in
incubate:
library("future")
plan(multisession, workers = 4)That’s it. You do not have to change any function calls.
incubate is future-aware. Consult the future-package
on CRAN for more information about futures and about supported
computation plans.
When you are done with the heavy computing, it is best practice to
release the parallel connections via plan(sequential).
The incubate package is found on CRAN and
development happens at Gitlab.
Use install.packages to install incubate
from CRAN as usual, i.e., install.packages("incubate")
should do.
To install its latest version from the main branch on Gitlab use the following R-code:
remotes::install_gitlab("imb-dev/incubate")To install a specific version, add the version tag after the name,
separated by a @, e.g. to install incubate in
version v1.1.9 use
remotes::install_gitlab("imb-dev/incubate@v1.1.9")The suffix @develop points to the latest
development version on Gitlab.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.