The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by METANET, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]metanet.ch.
Goals: create a unified interface for regression standardization to obtain estimates of causal effects such as the average treatment effect, or relative treatment effect.
stdReg2 and stdRegstdReg2 is the next generation of stdReg.
If you are happy using stdReg, you can continue using it
and nothing will change in the near future. With stdReg2 we
aim to solve similar problems but with nicer output, more available
methods, the possibility to include new methods, and mainly to make
maintenance and updating easier.
stdReg2 is available on CRAN and can be installed
with:
install.packages("stdReg2")You can install the development version of stdReg2 from
GitHub with:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("sachsmc/stdReg2")This is a basic example which shows you how to use regression standardization in a logistic regression model to obtain estimates of the causal risk difference and causal risk ratio:
library(stdReg2)
# basic example
# need to correctly specify the outcome model and no unmeasured confounders
# (+ standard causal assumptions)
set.seed(6)
n <- 100
Z <- rnorm(n)
X <- rnorm(n, mean = Z)
Y <- rbinom(n, 1, prob = (1 + exp(X + Z))^(-1))
dd <- data.frame(Z, X, Y)
x <- standardize_glm(
formula = Y ~ X * Z,
family = "binomial",
data = dd,
values = list(X = 0:1),
contrasts = c("difference", "ratio"),
reference = 0
)
x
#> Outcome formula: Y ~ X * Z
#> Outcome family: quasibinomial
#> Outcome link function: logit
#> Exposure: X
#>
#> Tables:
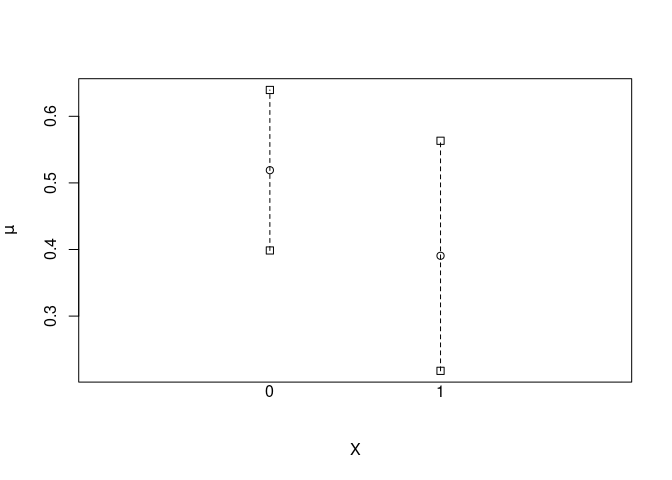
#> X Estimate Std.Error lower.0.95 upper.0.95
#> 1 0 0.519 0.0615 0.399 0.640
#> 2 1 0.391 0.0882 0.218 0.563
#>
#> Reference level: X = 0
#> Contrast: difference
#> X Estimate Std.Error lower.0.95 upper.0.95
#> 1 0 0.000 0.0000 0.000 0.00000
#> 2 1 -0.129 0.0638 -0.254 -0.00353
#>
#> Reference level: X = 0
#> Contrast: ratio
#> X Estimate Std.Error lower.0.95 upper.0.95
#> 1 0 1.000 0.000 1.000 1.000
#> 2 1 0.752 0.126 0.505 0.999
plot(x)
tidy(x)
#> X Estimate Std.Error lower.0.95 upper.0.95 contrast transform
#> 1 0 0.5190639 0.06149960 0.3985269 0.639600881 none identity
#> 2 1 0.3905311 0.08816362 0.2177336 0.563328623 none identity
#> 3 0 0.0000000 0.00000000 0.0000000 0.000000000 difference identity
#> 4 1 -0.1285328 0.06377604 -0.2535315 -0.003534039 difference identity
#> 5 0 1.0000000 0.00000000 1.0000000 1.000000000 ratio identity
#> 6 1 0.7523758 0.12604216 0.5053377 0.999413910 ratio identityFor more detailed examples, see the vignette “Estimation of causal effects using stdReg2”.
citation("stdReg2")
#> To cite package 'stdReg2' in publications use:
#>
#> Sachs M, Sjölander A, Gabriel E, Ohlendorff J, Brand A (2025).
#> _stdReg2: Regression Standardization for Causal Inference_. R package
#> version 1.0.3, <https://sachsmc.github.io/stdReg2/>.
#>
#> A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
#>
#> @Manual{,
#> title = {stdReg2: Regression Standardization for Causal Inference},
#> author = {Michael C Sachs and Arvid Sjölander and Erin E Gabriel and Johan Sebastian Ohlendorff and Adam Brand},
#> year = {2025},
#> note = {R package version 1.0.3},
#> url = {https://sachsmc.github.io/stdReg2/},
#> }These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.